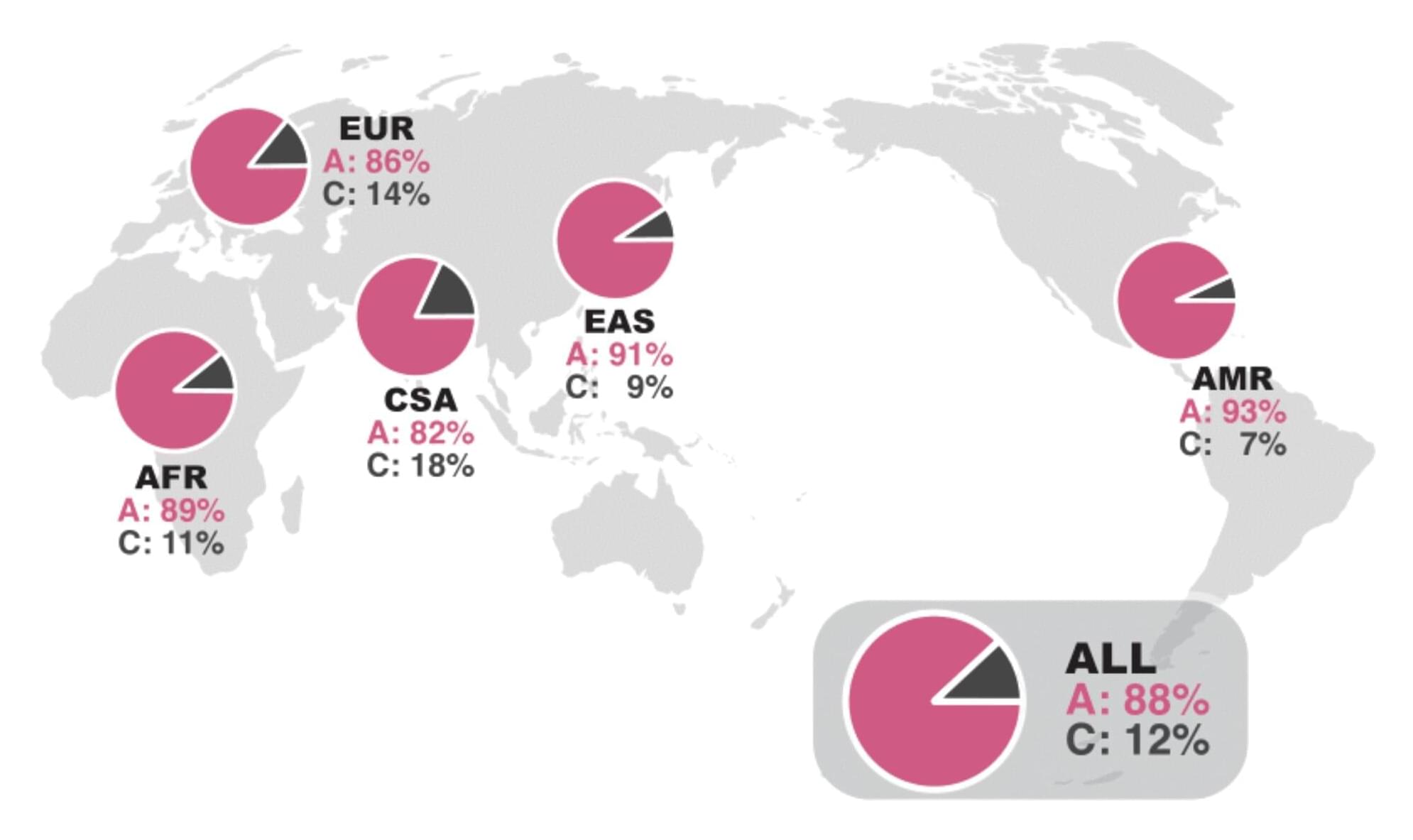
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is an incurable neurological disorder affecting motor neurons—nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord that control voluntary muscle movement and breathing.
Many ALS clinical trials, including those testing promising drugs, have fallen short of expectations—often because the extent of the disease can vary, and patients don’t respond the same way to medications.
But a new study led by scientists at Case Western Reserve University used stem cells created from ALS patients to target a specific gene as a kind of shut-off valve for what stresses nerve cells —and it worked.