It can track objects the size of a golf ball traveling at up 30000 kilometers per hour in LEO.
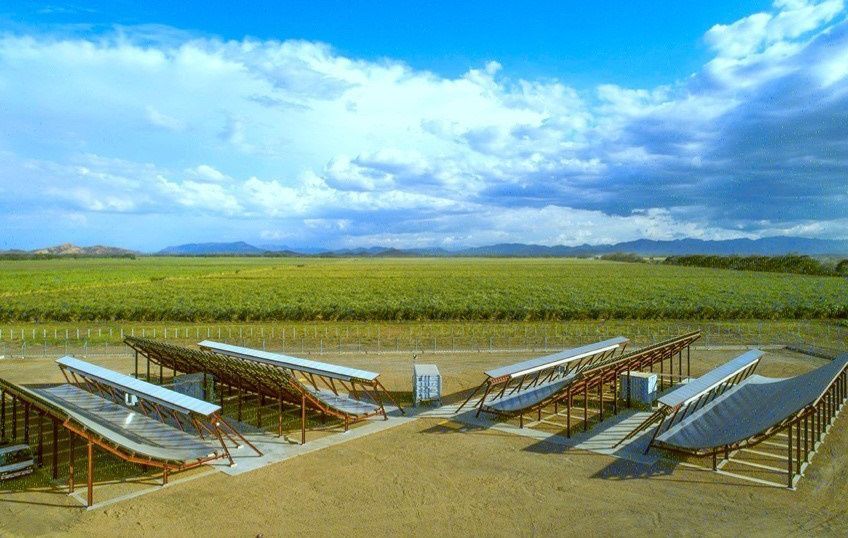
There’s a new giant space radar in Costa Rica that can track orbital debris as small as two centimeters. It was built by LeoLabs, a company that provides commercial radar tracking services for objects in Low Earth Orbit, which has declared the site fully operational less than a year after breaking ground. LeoLabs CEO Dan Ceperley said it’s the “most advanced commercial space radar of its kind” — one that’s capable of tracking objects the size of a golf ball traveling at up 30000 kilometers per hour.
The radar can keep an eye on both active satellites and space junk, which make up the vast majority of man-made objects found in LEO. They’re also the risks LeoLabs’ customers — made up of satellite operators, defense, space and regulatory agencies, insurance and scientific institutions — want to keep tabs on.
Space junk has increasingly occupied the Earth’s orbit over the past few decades, and it’s only bound to become a bigger issue in the coming years as private companies deploy more and more massive satellite constellations. Debris flying around in space is a huge threat to the ISS and future manned missions, giving rise to the need for a company like LeoLabs. Ed Lu, the company’s co-founder, explains that “[t]he number one danger to astronauts aboard the International Space Station has been and is today the risk of orbital debris that is too small to be tracked by the US Department of Defense going through the hull.”