This technology may someday power spacecraft, satellites, high-flying drones, and pacemakers.
Category: satellites – Page 179

Elon Musk Shares SpaceX Falcon 9 Image That Highlights Its True Size
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 is impressive, but based on launch photos it can be hard to get a sense of the true scale of the craft. On Wednesday, CEO Elon Musk shared an image that shows himself alongside three figures, standing next to a freshly-landed Falcon 9. The image gives a clear indication of how the craft appears in real life.
Musk shared the image below with the caption “At Falcon LZ-1 Vandenberg on Sunday night with the Base Commander. Support of [United States Air Force] much appreciated.” The image was taken just after Sunday’s launch, which saw the SAOCOM 1A satellite sent up from the Vandenberg Air Force Base, before the first stage booster landed on the firm’s brand new west coast landing pad. The whole craft measures 229.6 feet tall, with a 12-foot diameter. The composite fairing, which houses the satellite entering orbit, measures 43 feet with a 17-foot diameter.
See more: Elon Musk Shares Incredible Photos From SpaceX’s Landmark Falcon 9 Launch.
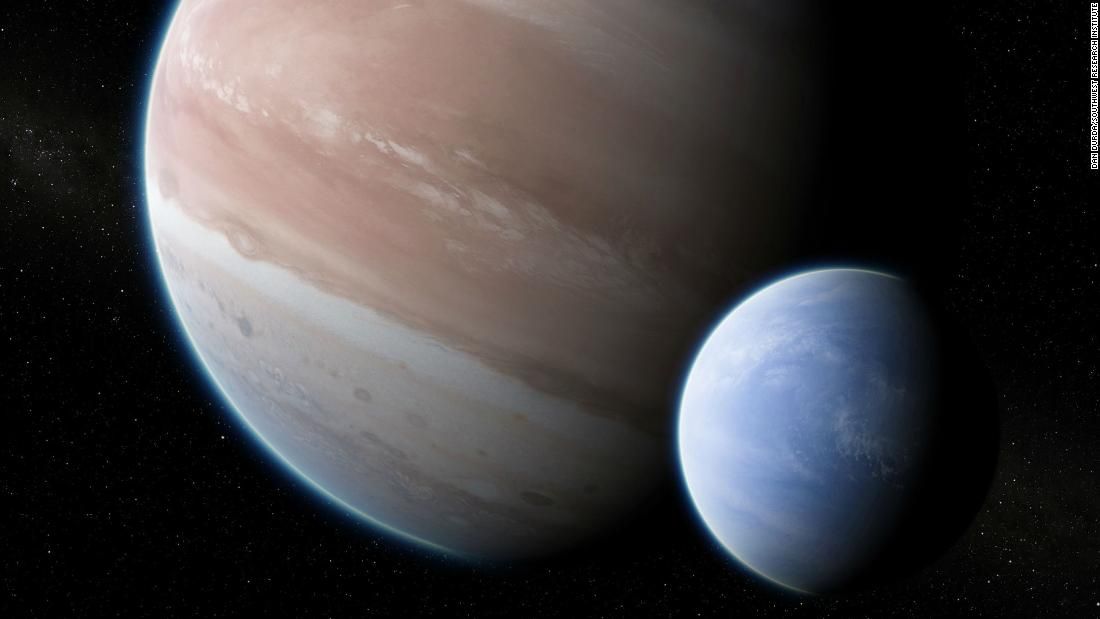

Is this the first moon found outside our solar system?
For the first time, astronomers have discovered what could be an exomoon, a moon outside our solar system. The exomoon was found around the gas giant exoplanet Kepler-1625b, which orbits a star 8,000 light-years from Earth.
Although moons are common in our solar system, which has nearly 200 natural satellites, the long search for interstellar moons has been an empty one. Astronomers have had success locating exoplanets around stars outside our solar system, but exomoons are harder to pinpoint because of their smaller size.
SpaceX’s Starlink satellites may use unique solar array deployment mechanism
Spotted on an official SpaceX T-shirt commemorating Starlink’s first two prototype satellites and corroborated through analysis of limited public photos of the spacecraft, SpaceX appears to be testing a relatively unique style of solar arrays on the first two satellites launched into orbit, known as Tintin A (Alice) and B (Bob).
It’s difficult to judge anything concrete from the nature of what may be immature prototypes, but SpaceX’s decision to take a major step away from its own style of solar expertise – Cargo Dragon’s traditional rigid panel arrays – is almost certainly motivated by a need to push beyond the current state of the art of satellite design and production.
SpaceX paints “X” on Western Falcon 9 landing pad for rocket recovery debut
According to NASASpaceflight.com, SpaceX has finished painting a fresh “X” on their newest Falcon 9 landing zone, located just a quarter of a mile from the company’s SLC-4 Vandenberg Air Force Base launch facilities.
In work in one shape or another since late 2014, mainly due to a lack of a pressing need for the pad, it’s looking increasingly likely that the West Coast landing zone (LZ) will be used for the first time on October 6th, shortly after a flight-proven Falcon 9 Block 5 rocket launches the Argentinian Earth-sensing satellite SAOCOM-1A.
SpaceX Falcon 9 launch with SAOCOM 1A coming up at Vandenberg next weekend. Static Fire test is NET October 2.

A solid industrial perspective in the Geo-Lunar space
Some industrial activities can give a ROI in a reasonable times. Recovery and reuse of space debris and wreckages, at least in its recovery part, is very much needed, for orbital safety. With proper orbital infrastructures, to capture debris, the logical next step will be to re-process them, getting powders for 3D printing, a platform for orbital ISRU, very first bricks of orbital factories. Assembly of satellites and vehicles in orbit is a large industrial perspective, that will decrease the cost of design, construction and launch: a first step towards a self sustaining space industrial development. There’s a number of in-orbit operations: transport and maintenance of satellites in orbit, refuelling stations, repair shops, orbital sites, orbital yards, spaceports, habitats. All the activities tied to space tourism, such as hotels and lodging facilities, passengers transportation systems (Earth-Orbit, inter-orbit, Earth-Moon). Products from zero gravity, asteroid and lunar mining are other very promising industrial activities, on which several startups were already born.
Priority to enabling technologies.
No longer whistling in the dark: Scientists uncover source of perplexing waves
Magnetic reconnection, the snapping apart and violent reconnection of magnetic field lines in plasma—the state of matter composed of free electrons and atomic nuclei—occurs throughout the universe and can whip up space storms that disrupt cell phone service and knock out power grids. Now scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) and other laboratories, using data from a NASA four-satellite mission that is studying reconnection, have developed a method for identifying the source of waves that help satellites determine their location in space.
Scientists receive $1.3 million to study new propulsion idea for spacecraft
Spacecraft and satellites could in future be launched into space without the need for fuel, thanks to a revolutionary new theory.
Dr Mike McCulloch, from the University of Plymouth, first put forward the idea of quantised inertia (QI) – through which he believes light can be converted into thrust – in 2007.
He has now received $1.3million from the United States Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) for a four-year study which aims to make the concept a reality.
‘Moonbeam’ at Last? Gov. Brown Says State Will Launch Satellite
(AP) — California Gov. Jerry Brown said Friday that the state plans to launch its “own damn satellite” into orbit to battle climate change.
The man the late Chicago columnist Mike Royko famously dubbed “Gov. Moonbeam” made the announcement at the conclusion of a two-day climate summit he organized in San Francisco.
Brown said state officials will work with the San Francisco-based company Planet Labs to develop a satellite to track climate-change causing pollutants. Brown said the earth-imaging company has launched 150 satellites.
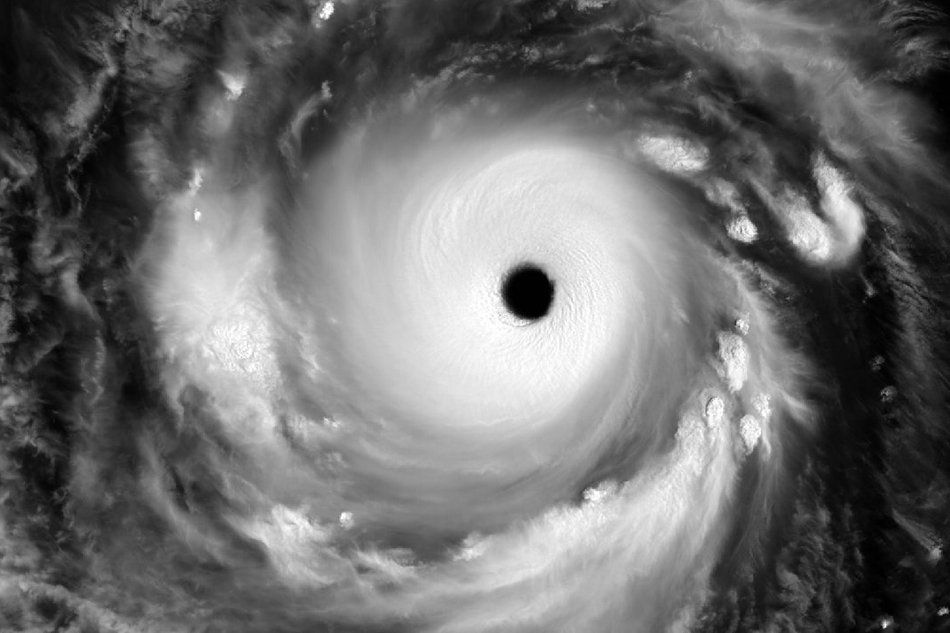

What NASA satellites found around Typhoon Ompong’s eye
Storms within a superstorm.
U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) satellites tracking Typhoon Ompong (international name Super Typhoon Mangkhut) have found powerful storms surrounding the eye of the tropical cyclone days before its landfall over northern Luzon.
On September 13, the MODIS instrument on the Aqua satellite looked at Ompong in infrared as it was approaching the Philippines, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center’s Rob Gutro said in a blog post.