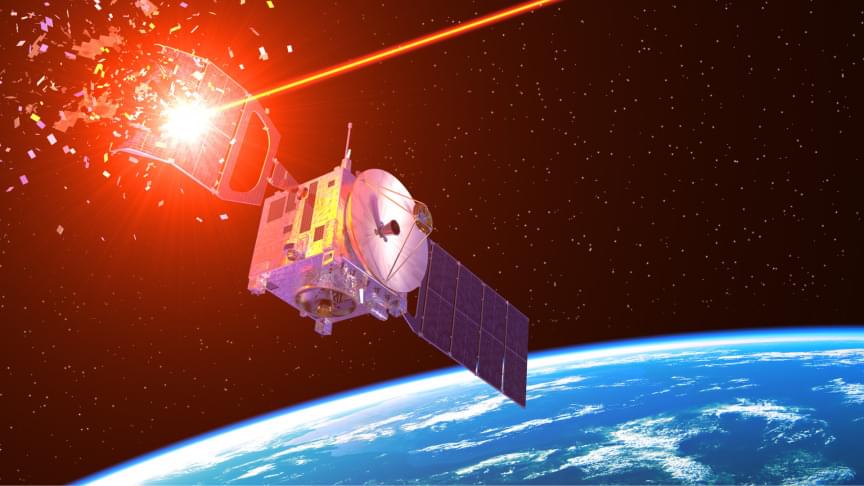
Will it succeed?An open-source investigation suggests that Russia is building a giant laser-based anti-satellite weapon near Zelenchukskaya in the southwest part of the country, Space.com reported. This will allow it a soft-kill option to take down adversarial satellites.
Instead of temporarily blurring sensors, Russia is going full throttle, looking to destroy optical sensors on satellites.