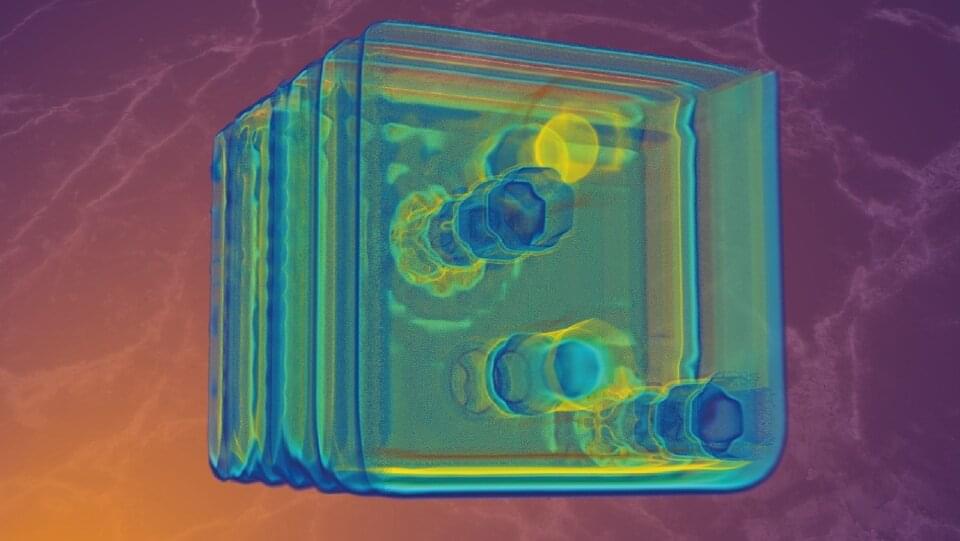
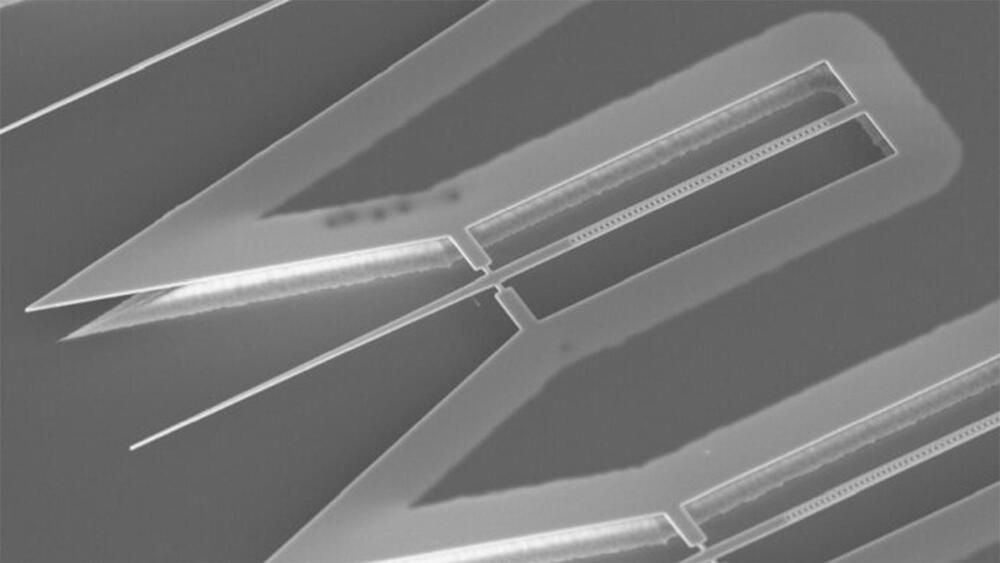
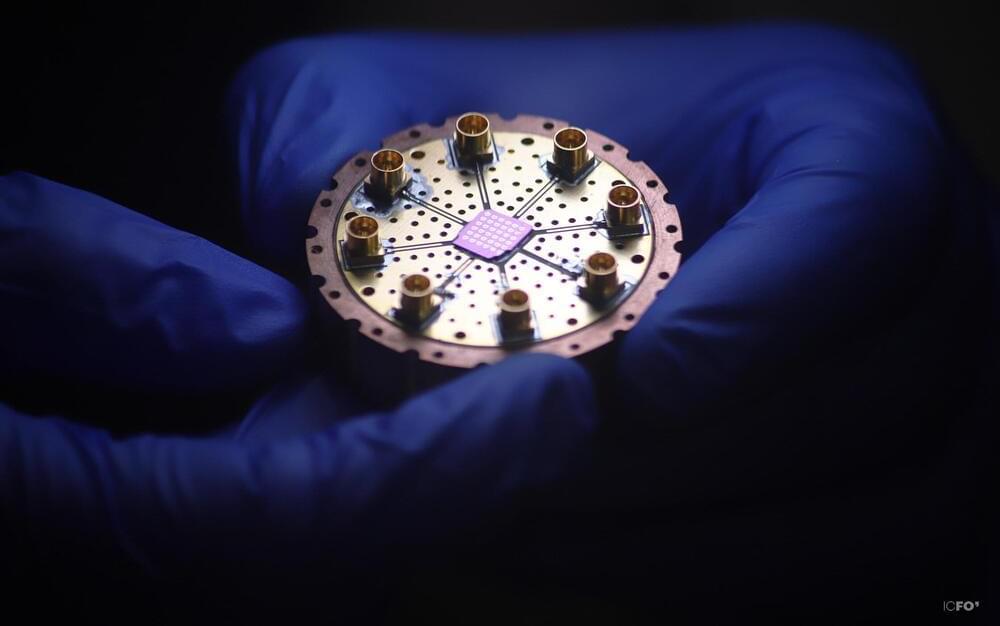
Loughborough University scientists are the first to demonstrate that a terahertz wave camera can capture 3D images of microscopic items hidden inside small objects.
Lead researcher Dr. Luana Olivieri says though the research is in the early stages, the team’s latest study could have “major implications for a range of fields with relevance in cancer screenings, security, and materials research.”
The research, which is in collaboration with Professor Marco Peccianti, Dr. Luke Peters, Dr. Juan S. Totero and a team of experts from the Emergent Photonics Research Center (EPicX), demonstrates that terahertz waves can be used to locate and recognize embedded objects and features, such as cracks and bubbles, in microscopic three-dimensional space. The study has been published in the journal ACS Photonics and is featured on the front cover of the latest issue, published today (June 21).