What can heat distribution within galaxy clusters, which often consist of hundreds to thousands of galaxies, teach astronomers about their formation and ev | Space


The U.S. House space committee moved a lunar time bill to a full House vote.
Berkeley Humanoid Lite is an open-source, budget-friendly humanoid robot created by UC Berkeley researchers to make robotics research easier for everyone. It’s a customizable, 3D-printed robot designed for researchers, teachers, and hobbyists. Unlike expensive, closed-source commercial robots (often over $100,000), it costs less than $5,000 by using common parts and desktop 3D printers. The robot’s motors and body use 3D-printed cycloidal gearboxes, keeping costs low while staying sturdy. You can buy all parts from online stores, and the design works with a 3D printer that has at least a 200 × 200 × 200 mm build space. It’s 80 cm
📰 Subscribe to UnHerd today at: https://bit.ly/3Qdkd5y.
UnHerd’s Flo Read meets Mars Society Founder, Robert Zubrin.
Watch it on the UnHerd website: https://unherd.com/watch-listen/how-humans-will-live-on-mars/
Listen to the podcast: https://plnk.to/unherd?to=page.
Renowned aerospace engineer and President of the Mars Society — which advocates for human exploration and colonisation of Mars — gives us his case for a manned mission to Mars, and all the challenges that getting to the Red Planet may entail. Is Elon Musk one of them?
Follow UnHerd on social media:

An engineered gut microbe can detoxify methylmercury, reducing the amount that passes into the brain and developing fetuses of mice fed a diet rich in fish, UCLA and UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography scientists have discovered.
“We envision the possibility that people could take a probiotic to offset the risk of consuming too much methylmercury, especially when pregnant,” said UCLA associate professor and director of the UCLA Goodman-Luskin Microbiome Center Elaine Hsiao, who is the senior author of a paper describing the research in the journal Cell Host & Microbe.
Mercury is a pollutant that enters water from several sources, the largest of which are human activities such as coal burning, artisanal gold mining and smelting, and wastes from consumer products. In the ocean, mercury transforms into a toxic form called methylmercury. It also biomagnifies, meaning that methylmercury concentrations in animal tissues increase up the food chain from algae-eaters to top predators like humans.
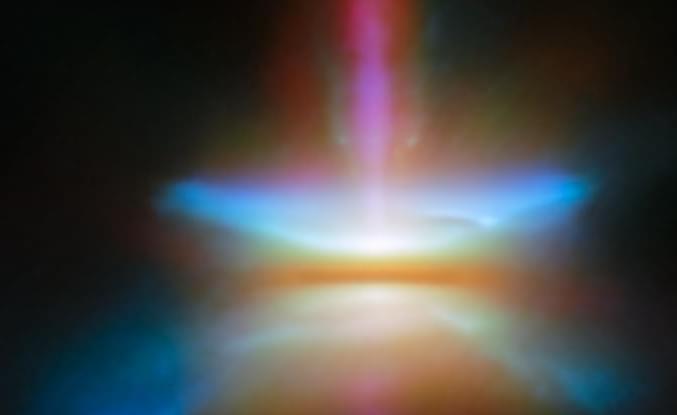


The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has been giving us a fabulous new view on the Universe since its launch.
This new image of the protostar HH30 is in amazing new detail thanks to the JWST. It was first discovered using the Hubble Space Telescope, but this Herbig-Haro object, which is a dark molecular cloud, is a perfect object for JWST.
The image shows the protoplanetary disk seen edge on, with a conical outflow of gas and dust, with a narrow jet blasting out into space.
What if gravity isn’t a force, but a computation? In this episode, we explore Dr. Melvin Vopson’s groundbreaking theory that gravity emerges from the universe’s effort to compress and optimize information. Discover how this idea connects with simulation theory, quantum physics, and the future of reality.
Paper link: https://pubs.aip.org/aip/adv/article/.… 00:00 Introduction 00:54 The Universe as a Computational System 02:18 Gravity as an Optimization Process 03:48 Implications and Similar Theories 07:20 Outro 07:39 Enjoy MUSIC TITLE : Starlight Harmonies MUSIC LINK : https://pixabay.com/music/pulses-star… Visit our website for up-to-the-minute updates: www.nasaspacenews.com Follow us Facebook: / nasaspacenews Twitter:
/ spacenewsnasa Join this channel to get access to these perks:
/ @nasaspacenewsagency #NSN #NASA #Astronomy#GravityTheory #InformationPhysics #MelvinVopson #SimulationHypothesis #DigitalUniverse #HolographicPrinciple #EntropicGravity #PhysicsExplained #ScienceNews #QuantumGravity #NewPhysics #ComputationalUniverse #BinaryReality #SpaceTime #QuantumMechanics #BlackHoleTheory #QuantumInformation #QuantumComputing #TheoreticalPhysics #ScienceBreakthrough #QuantumWorld #UnifiedTheory #SpaceExploration #Astrophysics #PhysicsToday #CosmosDecoded #EmergentGravity #ScienceFacts #GravityExplained #DigitalPhysics.
Chapters:
00:00 Introduction.
00:54 The Universe as a Computational System.
02:18 Gravity as an Optimization Process.
03:48 Implications and Similar Theories.
07:20 Outro.
07:39 Enjoy.
MUSIC TITLE : Starlight Harmonies.
MUSIC LINK : https://pixabay.com/music/pulses-star…
Visit our website for up-to-the-minute updates:
www.nasaspacenews.com.
Follow us.

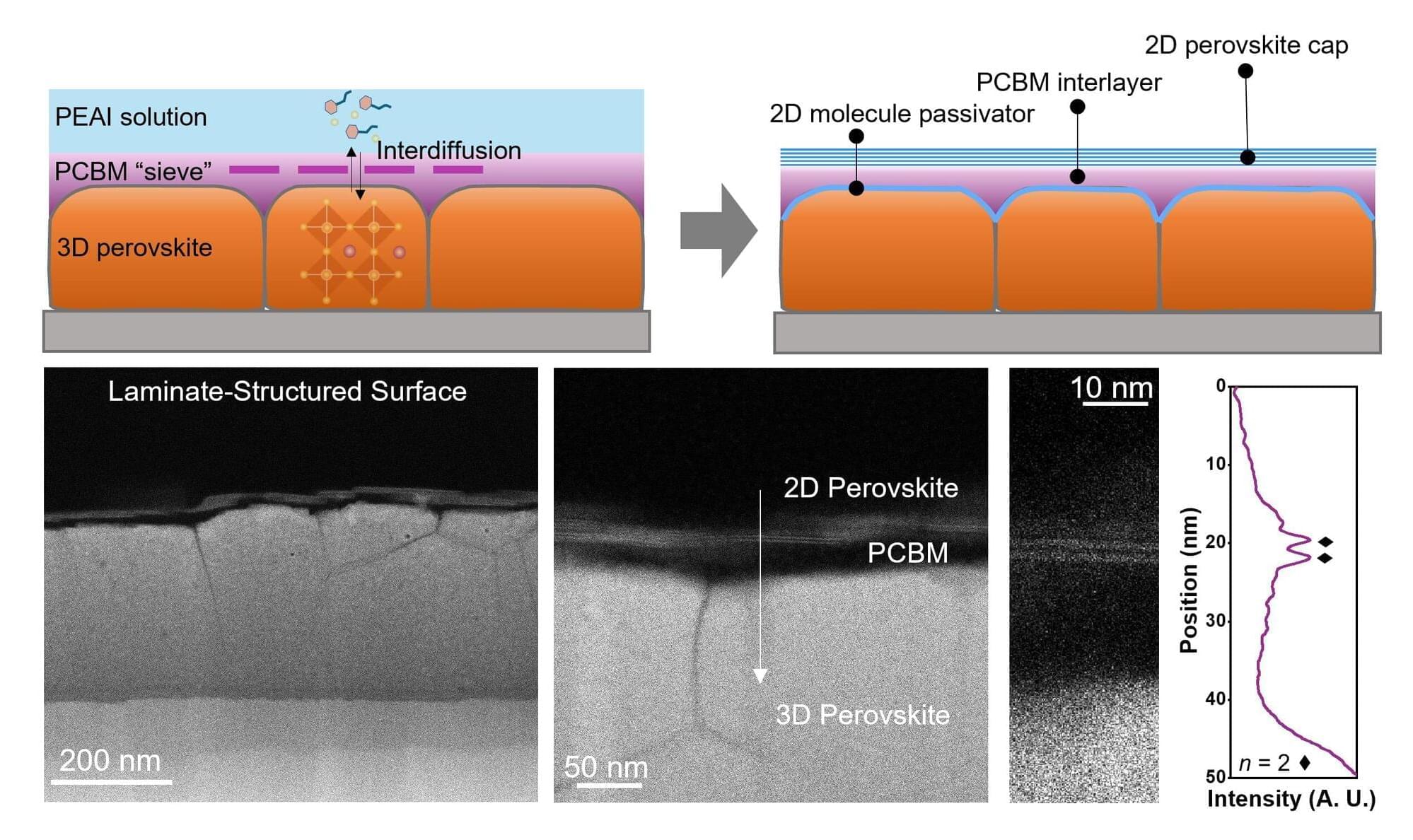
A collaborative research team from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) and the Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) has developed an innovative laminated interface microstructure that enhances the stability and photoelectric conversion efficiency of inverted perovskite solar cells. The research is published in the journal Nature Synthesis.
Perovskite solar cells have considerable potential to replace traditional silicon solar cells in various applications, including grid electricity, portable power sources, and space photovoltaics. This is due to their unique advantages, such as high efficiency, low cost, and aesthetic appeal.
The basic structures of perovskite solar cells are classified into two types: standard and inverted. The inverted structure demonstrates better application prospects because the electronic materials used in each layer are more stable compared to those in the standard configuration.