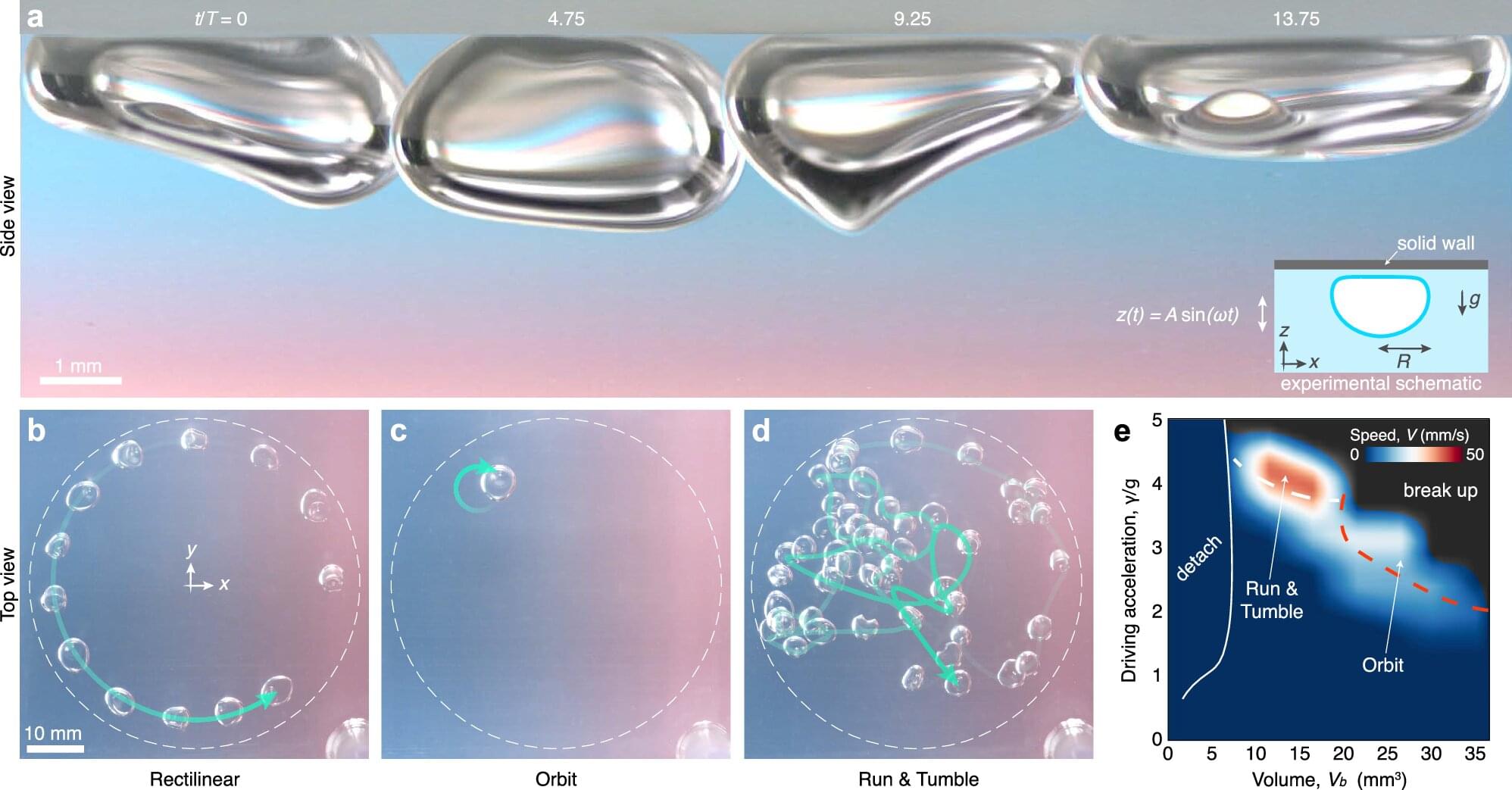
A team led by researchers at UNC-Chapel Hill have made an extraordinary discovery that is reshaping our understanding of bubbles and their movement. Picture tiny air bubbles inside a container filled with liquid. When the container is shaken up and down, these bubbles engage in an unexpected, rhythmic “galloping” motion—bouncing like playful horses and moving horizontally, even though the shaking occurs vertically.
This counterintuitive phenomenon, revealed in a new study published in Nature, has significant implications for technology, from cleaning surfaces to improving heat transfer in microchips and even advancing space applications.
These galloping bubbles are already garnering significant attention: their impact in the field of fluid dynamics has been recognized with an award for their video entry at the most recent Gallery of Fluid Motion, organized by the American Physical Society.