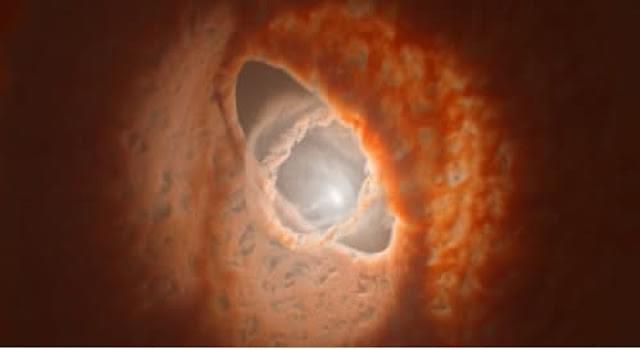
Perched in the constellation Orion, 1,300 light-years from Earth, lies GW Orionis, a unique triple-star solar system. Unlike most known systems, GW Orionis features two stars orbiting each other closely, while a third star circles at a much greater distance. Surrounding these stars are three enormous, misaligned rings of planet-forming dust, creating a striking bullseye pattern in the sky.
Recent studies, published in Science and The Astrophysical Journal Letters, suggest that these rings may harbor a young planet—or the makings of one. This celestial body could explain the dramatic misalignment of the system’s inner ring, which appears to wobble like a broken gyroscope. If confirmed, this would be the first known planet orbiting three stars simultaneously.
Nienke van der Marel, astrophysicist and co-author of the May 21 study, noted that the combined gravitational pull of the three stars alone cannot account for the rings’ behavior. Instead, the presence of a planet carving a gap in the disk could be disrupting the system’s balance.