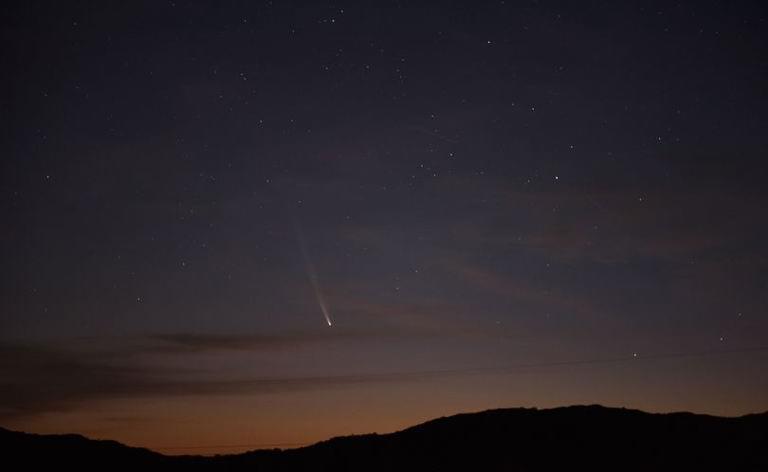
A rare comet could be visible to the naked eye in the sky for several nights as it orbits around the sun before disappearing for another 80,000 years.


TL;DR
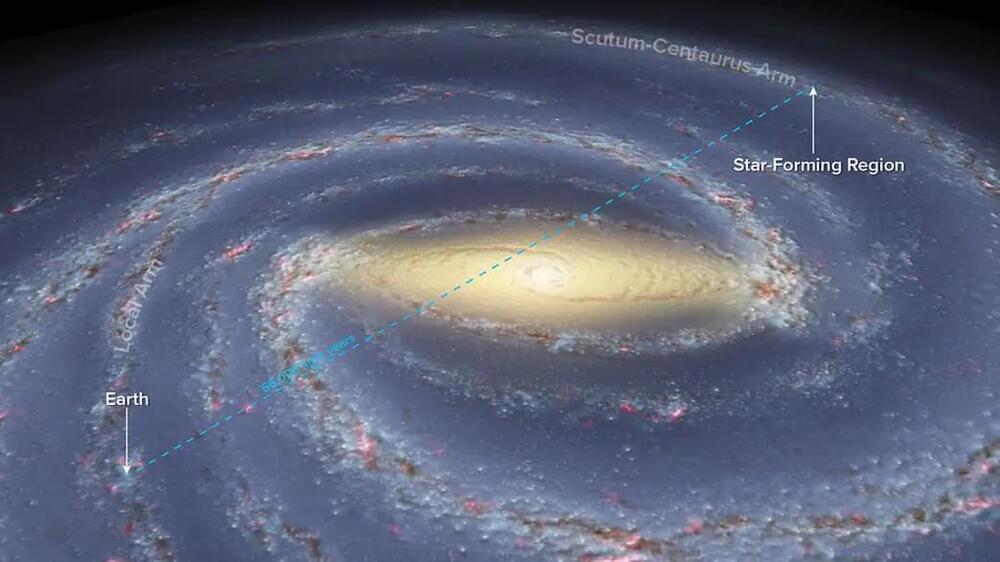
Using a precise parallax method, scientists measured the distance to a star-forming region 66,000 light-years away on the far side of the Milky Way. This discovery, using the Very Long Baseline Array, confirmed the existence of the Scutum-Centaurus Arm and uncovered its undulating shape. The interstellar dust obstructing visible light made this feat more challenging, but tracking molecules like methanol and water helped scientists achieve this. This is part of a larger effort to map the entire Milky Way, with about a quarter still unexplored, offering more insights into the galaxy’s true structure.
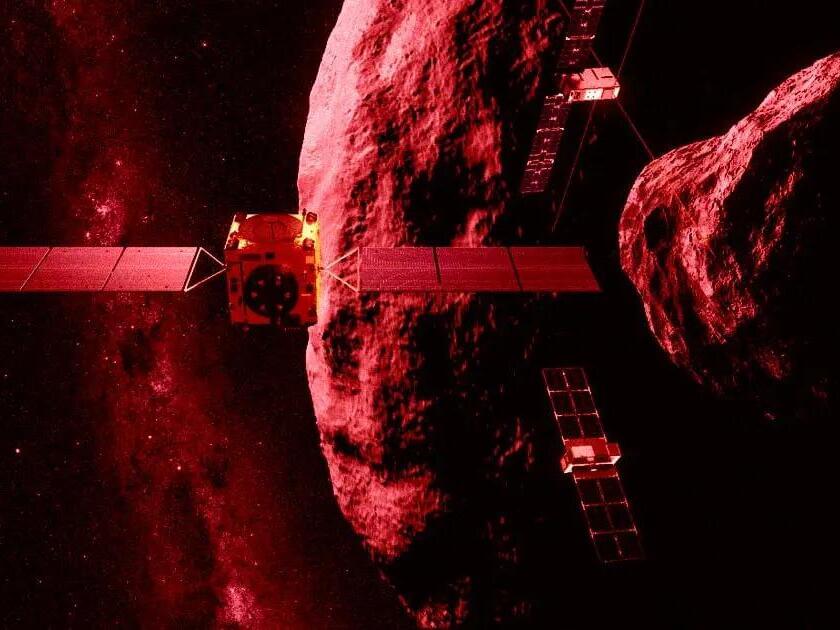

The European Space Agency (ESA) just launched its much-anticipated effort to explore the wreckage of the asteroid Dimorphos, the cosmic body that NASA successfully obliterated last year during its pioneering planetary defense test in 2022. The “crash scene” surveillance team includes the spacecraft Hera as well as two tiny cubesats,…

In 2023, the NASA OSIRIS-REx mission returned a sample of dust and rocks collected on the near-Earth asteroid Bennu. In addition to the information about the universe gleaned from the sample itself, the data generated by OSIRIS-REx might also present an opportunity to probe new physics. As described in Communications Physics, an international research team led by Los Alamos National Laboratory used the asteroid’s tracking data to study the possible existence of a fifth fundamental force of the universe.
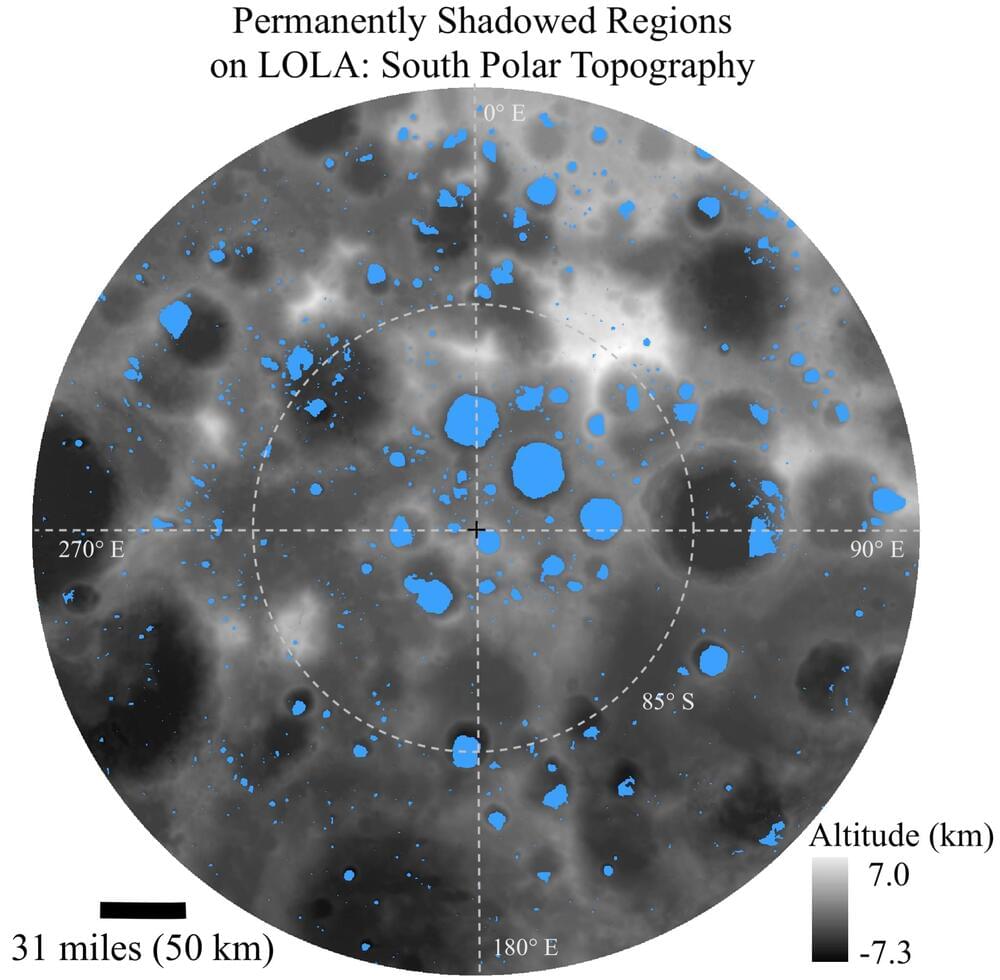
Scientists have discovered far more water ice deposits near the Moon’s south pole than previously hypothesized, which could help astronauts on future crewed missions to the lunar surface.
How much water ice could be present within the permanently shadowed regions (PSRs) near the Moon’s south pole? This is what a recent study published in The Planetary Science Journal hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated how water ice deposits could exist hundreds of miles beyond the PSRs located near the south pole, as opposed to close proximity to the south pole as previous studies have hypothesized. This study holds the potential to enable future crewed missions to locate water ice deposits, which could assist in water usage, oxygen generation from electrolysis, fuel, and energy.
For the study, the researchers used NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) to obtain data on hydrogen concentration within several PSR craters near the lunar south pole, along with potential sources of the hydrogen concentrations. The reason PSRs are targets for water ice is due to their extreme depths where sunlight doesn’t reach, resulting in temperatures well below-freezing and the accumulation of water ice over millions, if not billions, of years. The team found that hydrogen concentrations existed in craters several hundred miles from the direct south pole and with temperatures below 75 Kelvin (−198.15 degrees Celsius/-324.67 degrees Fahrenheit). Additionally, the team also concluded that the likely sources of the hydrogen concentrations were from a variety of sources, including solar radiation, comets, and meteorites.
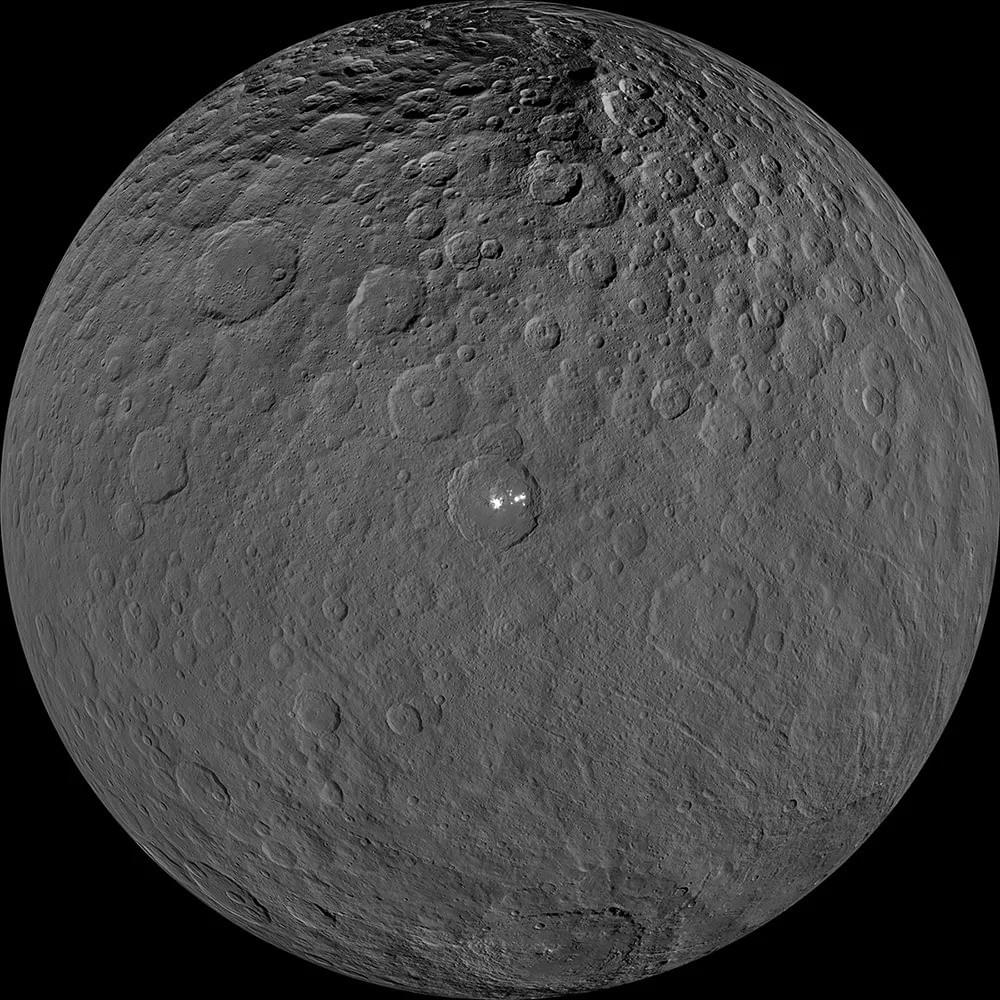

Ian Pamerleau: “We used multiple observations made with Dawn data as motivation for finding an ice-rich crust that resisted crater relaxation on Ceres. Different surface features (e.g., pits, domes and landslides, etc.) suggest the near subsurface of Ceres contains a lot of ice.”
Was the dwarf planet Ceres once an ocean world like Europa and Enceladus? If so, how did it become the cratered and icy world we see today? This is what a recent study published in Nature Astronomy hopes to address as a team of researchers from Purdue University and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) investigated the formation and evolution of the internal geological processes of Ceres and how this could help scientists better understand ocean worlds throughout the solar system.
“We think that there’s lots of water-ice near Ceres surface, and that it gets gradually less icy as you go deeper and deeper,” said Dr. Mike Sori, who is an assistant professor in the Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences at Purdue University and a co-author on the study. “People used to think that if Ceres was very icy, the craters would deform quickly over time, like glaciers flowing on Earth, or like gooey flowing honey. However, we’ve shown through our simulations that ice can be much stronger in conditions on Ceres than previously predicted if you mix in just a little bit of solid rock.”
https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/153422/sprites-camera-action.
An astronaut on the International Space Station captured a red sprite over North America, a rare atmospheric phenomenon associated with powerful lightning.
This event, visible from space, was recorded through a timelapse video that spans over several U.S. states. The sequence also highlights other weather phenomena and contributes to NASAs Spritacular project, which aims to better understand these elusive events.
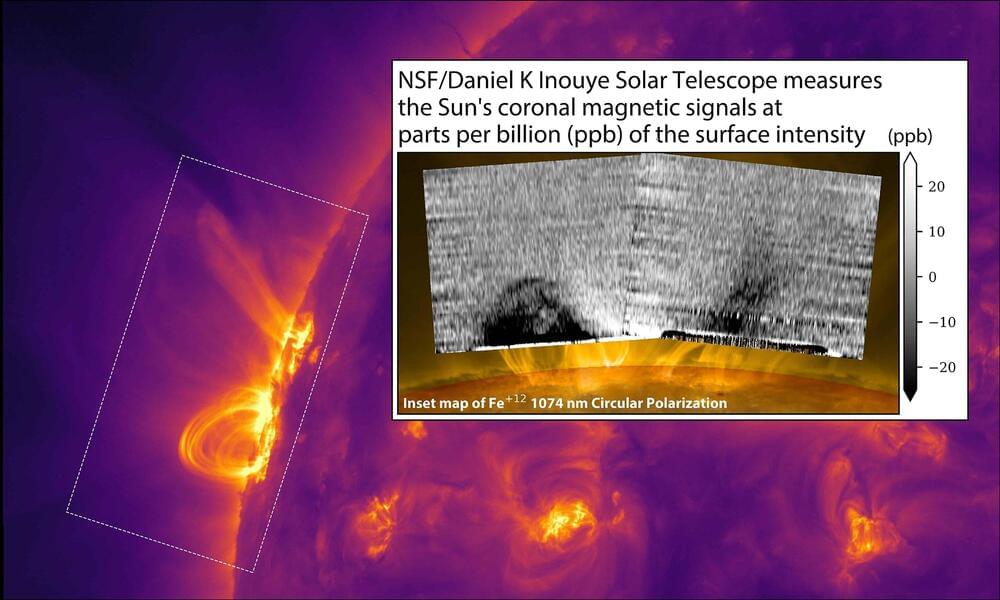
The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope, the world’s most powerful solar telescope, designed, built, and operated by the NSF National Solar Observatory (NSO), achieved a major breakthrough in solar physics by directly mapping the strength of the magnetic field in the solar corona, the outer part of the solar atmosphere that can be seen during a total eclipse. This breakthrough promises to enhance our understanding of space weather and its impact on Earth’s technology-dependent society.
The corona: the launch pad of space weather.
The Sun’s magnetic field generates regions in the Sun’s atmosphere, often rooted by sunspots, that store vast amounts of energy that fuel explosive solar storms and drive space weather. The corona, the Sun’s outer atmosphere, is a superheated realm where these magnetic mysteries unfold. Mapping coronal magnetic fields is essential to understanding and predicting space weather — and to protect our technology in Earth and space.