“Through our simulated impacts, we found that the pure water froze too quickly in a vacuum to effect meaningful change, but salt and water mixtures, or brines, stayed liquid and flowing for a minimum of one hour,” said Dr. Michael J. Poston.
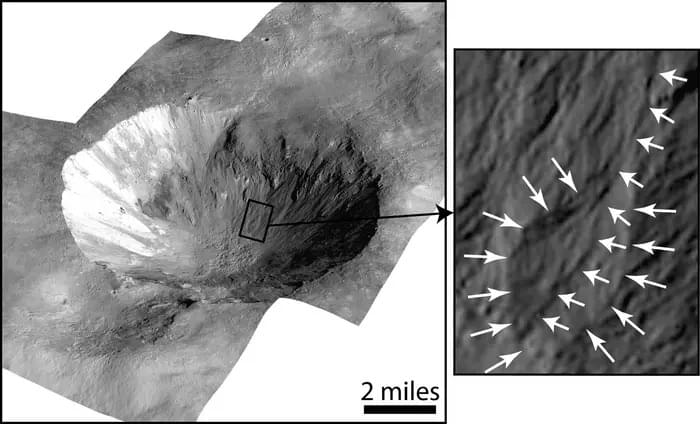
How does extra salty water, also known as briny water, form and evolve on worlds without atmospheres, such as asteroids and moons? This is what a recent study published in The Planetary Science Journal hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated how briny water could still flow for a period of time on the asteroid Vesta after large impacts resulted in the melting of subsurface ice. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the geological and chemical processes on planetary bodies without atmospheres and what this could mean for finding life as we know it.
“We wanted to investigate our previously proposed idea that ice underneath the surface of an airless world could be excavated and melted by an impact and then flow along the walls of the impact crater to form distinct surface features,” said Dr. Jennifer Scully, who is a planetary geologist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and a co-author on the study.
For the study, the researchers used a JPL test chamber to analyze how liquid samples responded to rapid drops in atmospheric pressure on the asteroid Vesta, thus simulating the conditions of a high-speed impact, which also includes the very brief creation of an atmosphere resulting from that impact. In the end, the researchers made some intriguing findings that could help scientists better understand the geological and chemical processes that occur on planetary bodies without atmospheres.





 $\sim$15 arcsec resolution) and catalogues of about three million source components with spectral index and polarisation information. In this paper, we present a description of the RACS survey and the first data release of 903 images covering the sky south of declination
$\sim$15 arcsec resolution) and catalogues of about three million source components with spectral index and polarisation information. In this paper, we present a description of the RACS survey and the first data release of 903 images covering the sky south of declination  $+41^\circ$ made over a 288-MHz band centred at 887.5 MHz.
$+41^\circ$ made over a 288-MHz band centred at 887.5 MHz.