Sep 7, 2023
Meet China’s new ‘Force’ gun that can move things from afar
Posted by Gemechu Taye in categories: space, tractor beam
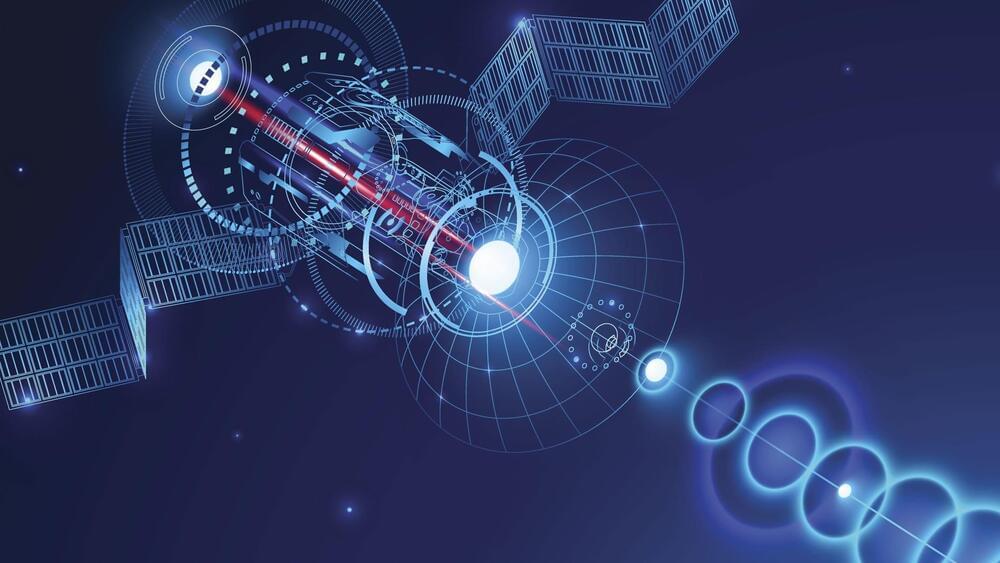
Chinese scientists have apparently developed a new kind of magnetized coaxial gun that can generate magnetized plasma rings to move stuff at a distance without physical contact.
Chinese scientists are working on a device that uses plasma rings to move objects at a distance. Touted as possibly being used for contactless satellite recovery, delivery, or space object deflection, the team behind the program is confident the device would work in principle, the South China Morning Post.
Likened to the “Jedi” abilities of ‘Force Push’ and ‘Force Pull’ in the science fiction franchise ‘Star Wars’ (though possibly closer in concept to an actual ‘tractor beam’), the device could prove revolutionary for many industries if proven viable.