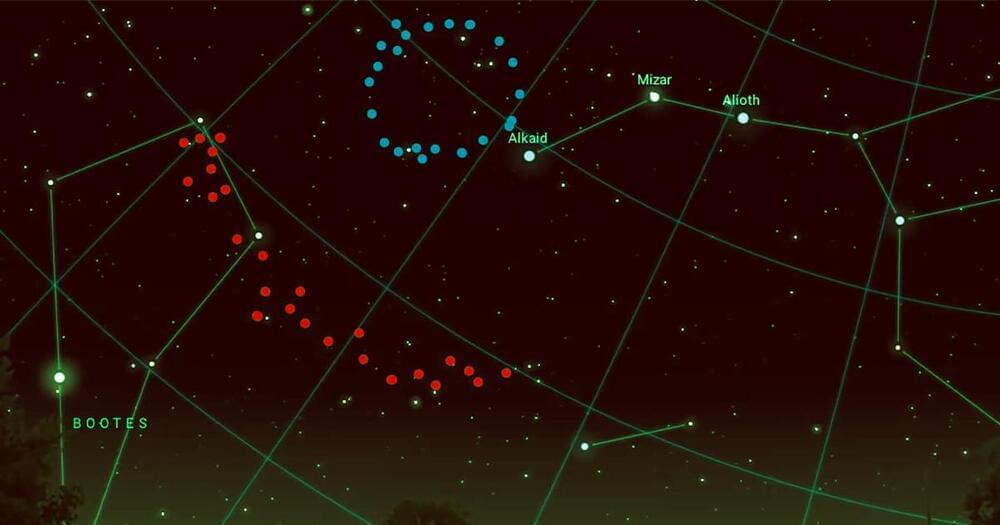
Lurking some nine billion light years away from Earth is what appears to be a so-called cosmic megastructure in the shape of an enormous ring. It’s so large that its existence should be impossible, according to new research reported on by The Guardian, challenging a fundamental assumption of our understanding of the Universe.
Known as the “Big Ring,” the structure spans an astonishing 1.3 billion light years in diameter — a significant portion of the observable Universe’s estimated size of 94 billion light years. By contrast, the largest known galaxy is a “mere” 16 million light years across. If it were visible in the night sky to the naked eye, the Big Ring would be equal in diameter to fifteen full moons. Succinctly put: it’s unfathomably huge.
The unpublished findings, presented at the annual meeting of the American Astronomical Society on Thursday, add to a growing list of inexplicably large structures that remain confounding — if not controversial — to scientists.