Astronomers have just solved a long-standing mystery about a rare, rapidly spinning neutron star known as PSR J1023+0038. Using NASA’s IXPE telescope and a fleet of observatories, scientists discovered that the system’s intense X-rays don’t come from its glowing accretion disk as previously belie
Category: space – Page 38
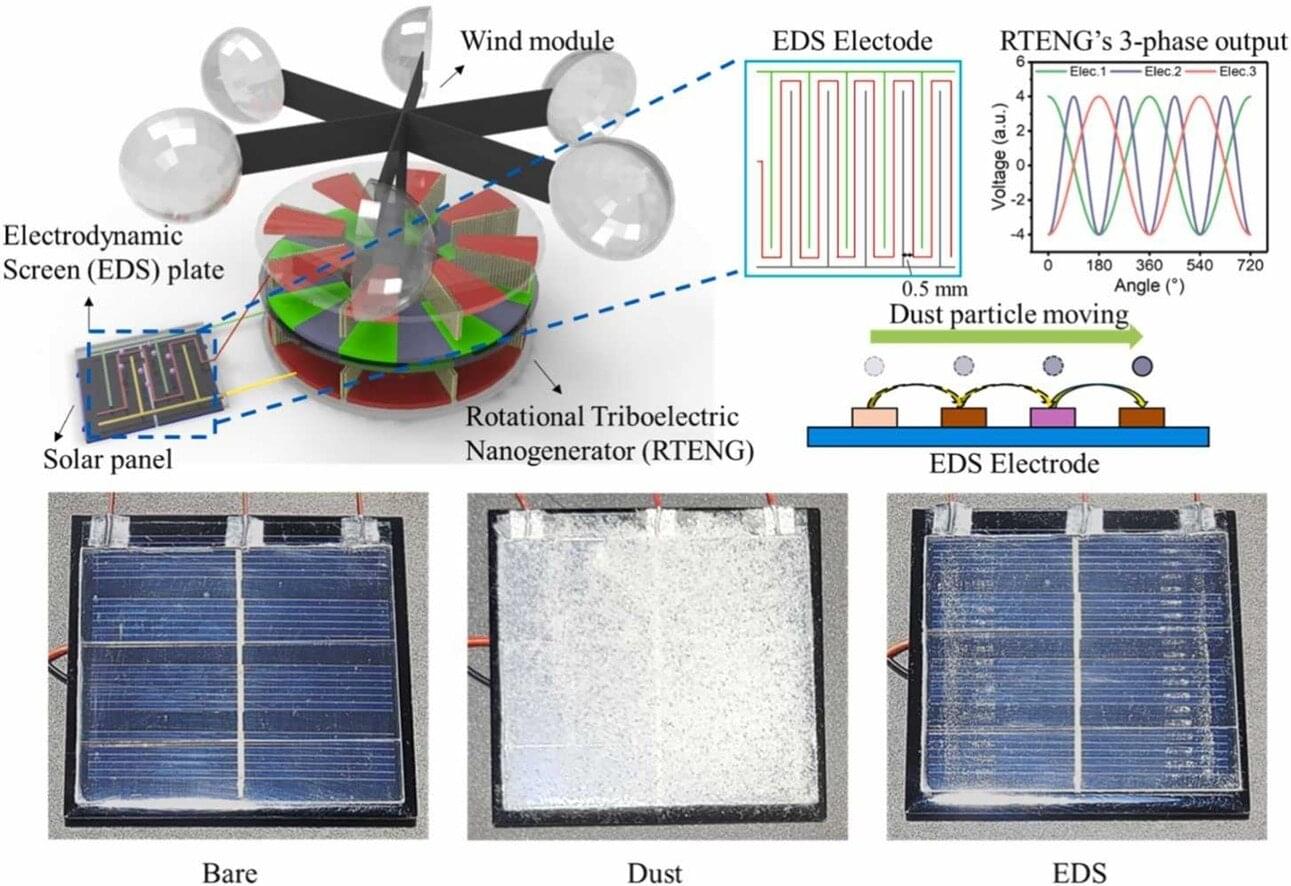
Self-powered solar panels remove dust using wind-generated electricity
A collaborative research team has successfully developed a self-powered pollution prevention technology that can remove pollutants from the surface of solar panels without external power. This technology uses a wind-powered rotational triboelectric nanogenerator to generate power and combines said power with electrodynamic screen (EDS) technology to move dust in the desired direction for removal.
The findings are published in the journal Nano Energy. The team was led by Professor Juhyuck Lee from the Department of Energy Science and Engineering, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology, along with Dr. Wanchul Seung at Global Technology Research, Samsung Electronics.
The dust that gathers on the surface of solar panels causes a significant reduction in power production efficiency. EDS technology, designed to address this problem, uses electric fields to remove dust from the surface, and it is noted for environments that are not easily accessible, such as deserts, mountains, and space, as it does not require cleaning equipment or personnel. Traditional EDS technology, however, requires high voltage and, consequently, external power, and it has the disadvantage of additional maintenance costs.

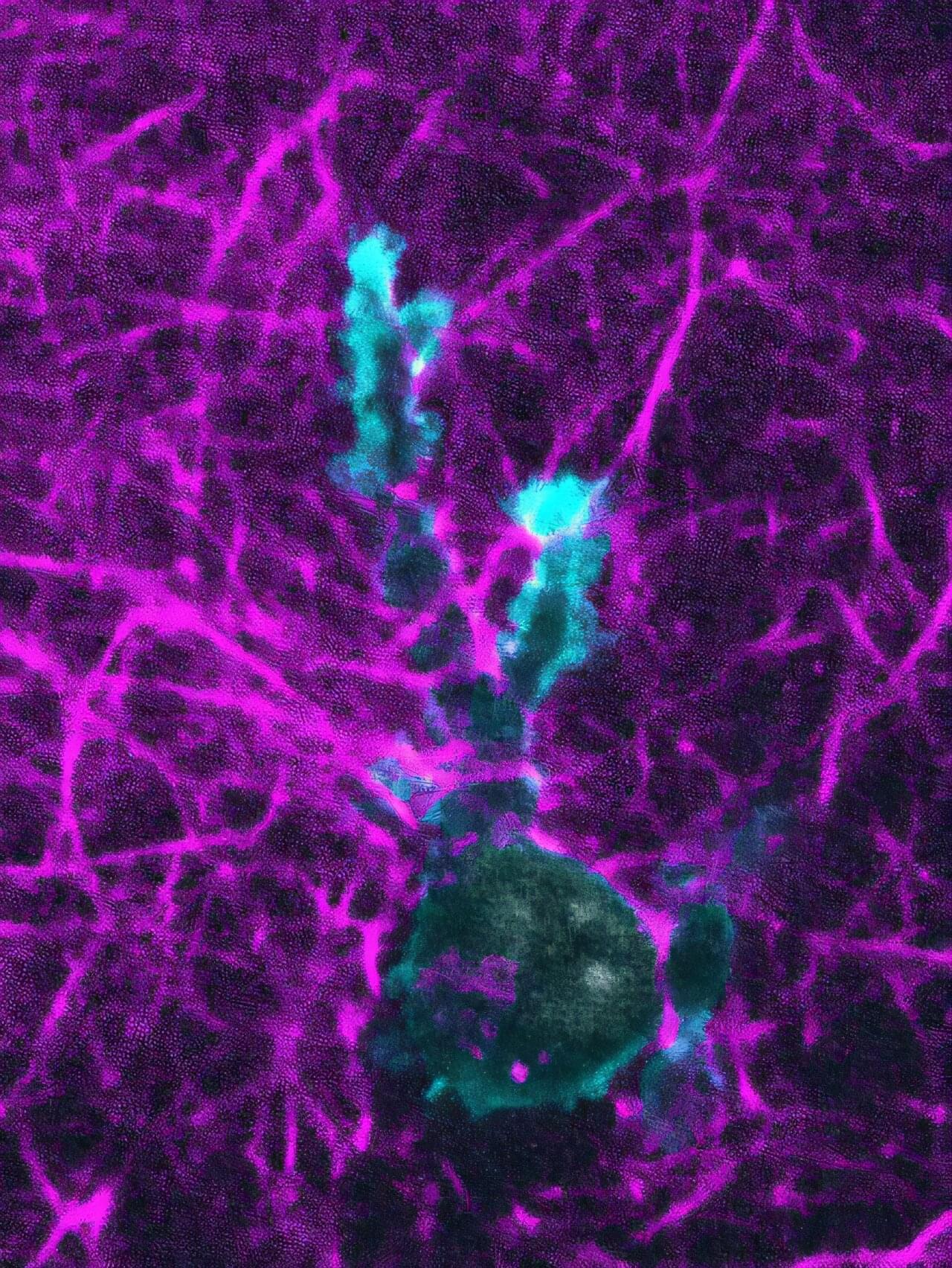
Immune cells turn into ‘mini-Hulks’ to push away tissue and make space when migrating
Immune responses rely on the efficient movement of immune cells within the complex and geometrically unpredictable three-dimensional tissues that make up our bodies.
Research by the Sixt group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) unveils how immune cells use their cytoskeleton to exert forces on their surrounding environment to push their way through tissues.
The findings were published in Nature Immunology.
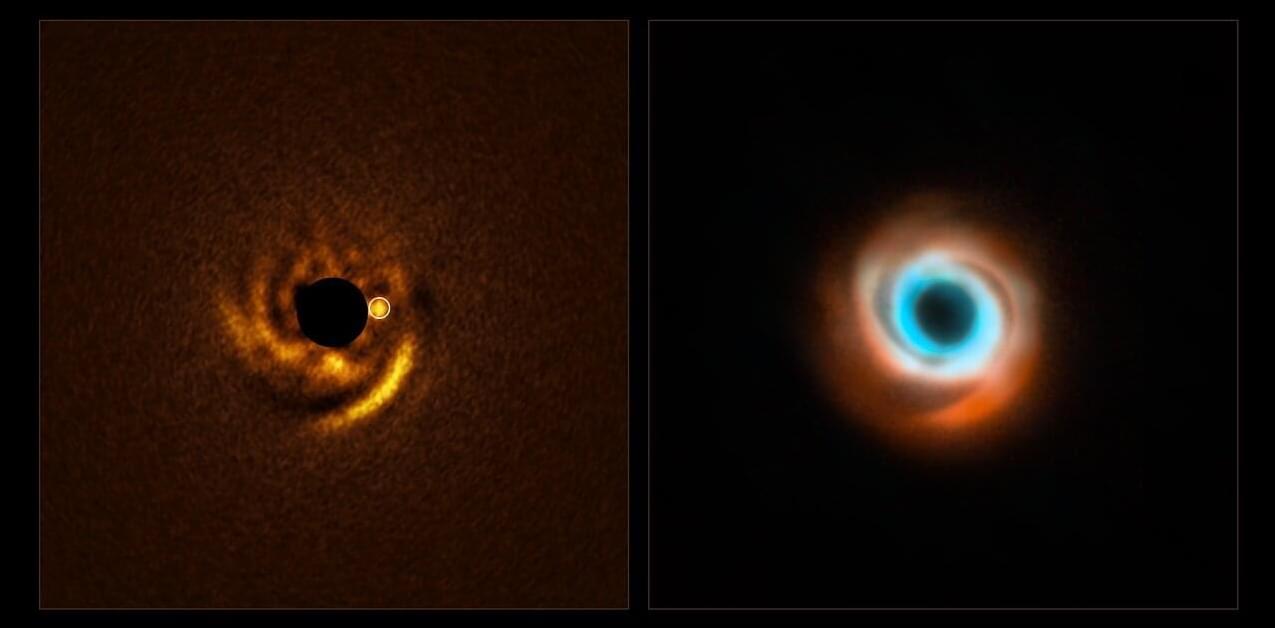


Cosmic sculptor: Astronomers spot young planet shaping spiral arms in dusty stellar disk
Astronomers may have caught a still-forming planet in action, carving out an intricate pattern in the gas and dust that surrounds its young host star. Using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), they observed a planetary disk with prominent spiral arms, finding clear signs of a planet nestled in its inner regions. This is the first time astronomers have detected a planet candidate embedded inside a disk spiral.
“We will never witness the formation of Earth, but here, around a young star 440 light-years away, we may be watching a planet come into existence in real time,” says Francesco Maio, a doctoral researcher at the University of Florence, Italy, and lead author of this study, published in Astronomy & Astrophysics.
The potential planet-in-the-making was detected around the star HD 135344B, within a disk of gas and dust around it called a protoplanetary disk. The budding planet is estimated to be twice the size of Jupiter and as far from its host star as Neptune is from the sun. It has been observed shaping its surroundings within the protoplanetary disk as it grows into a fully formed planet.

Dawn of a New Solar System: Watch Planets Begin to Form 1300 Light-Years Away
In a cosmic first, scientists watched planet-forming materials begin to solidify around a newborn star, offering a peek into what our Solar System may have looked like at birth. It’s a stunning replay of planetary evolution, just 1300 light-years away.

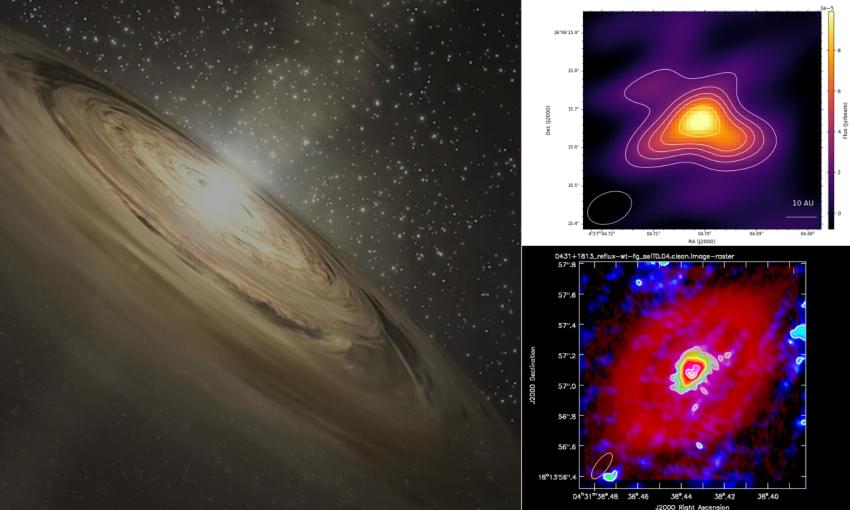
Astronomers Catch Planets in the Act of Being Born
Astronomers have spotted centimeter-sized “pebbles” swirling around two infant stars 450 light-years away, revealing the raw ingredients of planets already stretching to Neptune-like orbits. Using the UK’s eMERLIN radio array, the PEBBLeS project found these rocky seeds in unprecedented detail, bridging the elusive gap between dusty discs and fully-formed worlds. The discovery hints that systems even larger than our own could be commonplace and sets the stage for the upcoming Square Kilometre Array to map hundreds more planetary nurseries.
A fascinating glimpse into how a solar system like our own is born has been revealed with the detection of planet-forming ‘pebbles’ around two young stars.
These seeds to make new worlds are thought to gradually clump together over time, in much the same way Jupiter was first created 4.5 billion years ago, followed by Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.