A mysterious new interstellar object, 3I/ATLAS, was discovered in July. It turns out that wasn’t the first time our telescopes spotted it.
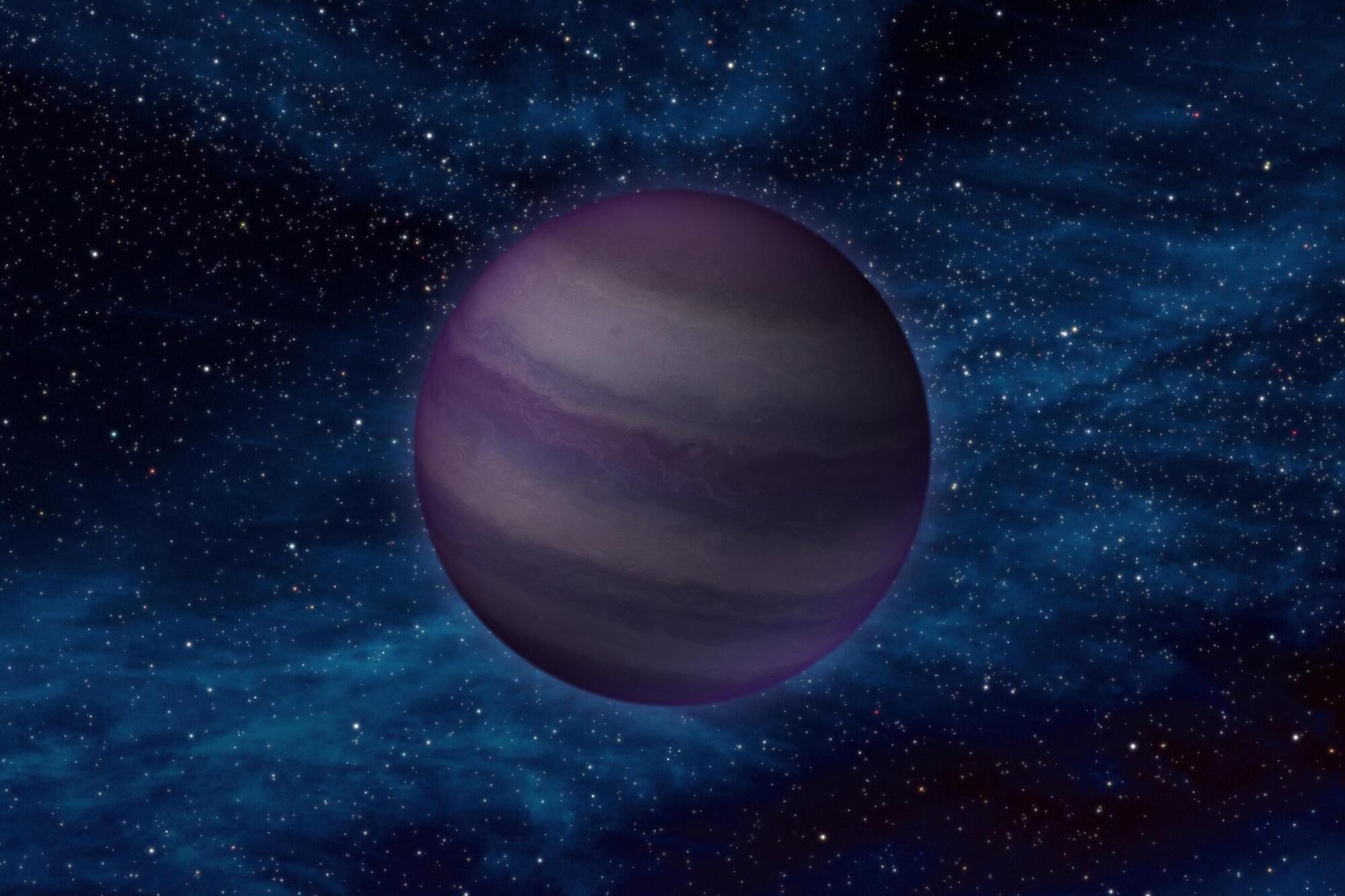



Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the Gemini Observatory, European astronomers have observed a nearby cold brown dwarf known as WISE 1738. Results of the observational campaign, published July 16 on the arXiv preprint server, deliver important insights into the physical properties and atmospheric chemistry of this object.
Questions to inspire discussion.
🍳 Q: What can diners expect in terms of food quality? A: The diner emphasizes local sourcing, natural ingredients, and fresh in-house preparation, with a menu designed by Eric Greensman, a professional chef.
Unique Offerings.
🤖 Q: What unique attractions does the Tesla diner offer? A: The diner showcases a fully functional Optimus robot on display and offers Tesla merchandise for purchase.
🍗 Q: Are there any special menu items or services? A: The diner features a self-service club with fried chicken and waffles, a souvenir cup for purchase, and a Tesla burger on the menu.
Practical Amenities.

Earth is spinning faster this summer, making the days marginally shorter and attracting the attention of scientists and timekeepers.
July 10 was the shortest day of the year so far, lasting 1.36 milliseconds less than 24 hours, according to data from the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service and the US Naval Observatory, compiled by timeanddate.com. More exceptionally short days are coming on July 22 and August 5, currently predicted to be 1.34 and 1.25 milliseconds shorter than 24 hours, respectively.
The length of a day is the time it takes for the planet to complete one full rotation on its axis —24 hours or 86,400 seconds on average. But in reality, each rotation is slightly irregular due to a variety of factors, such as the gravitational pull of the moon, seasonal changes in the atmosphere and the influence of Earth’s liquid core. As a result, a full rotation usually takes slightly less or slightly more than 86,400 seconds — a discrepancy of just milliseconds that doesn’t have any obvious effect on everyday life.
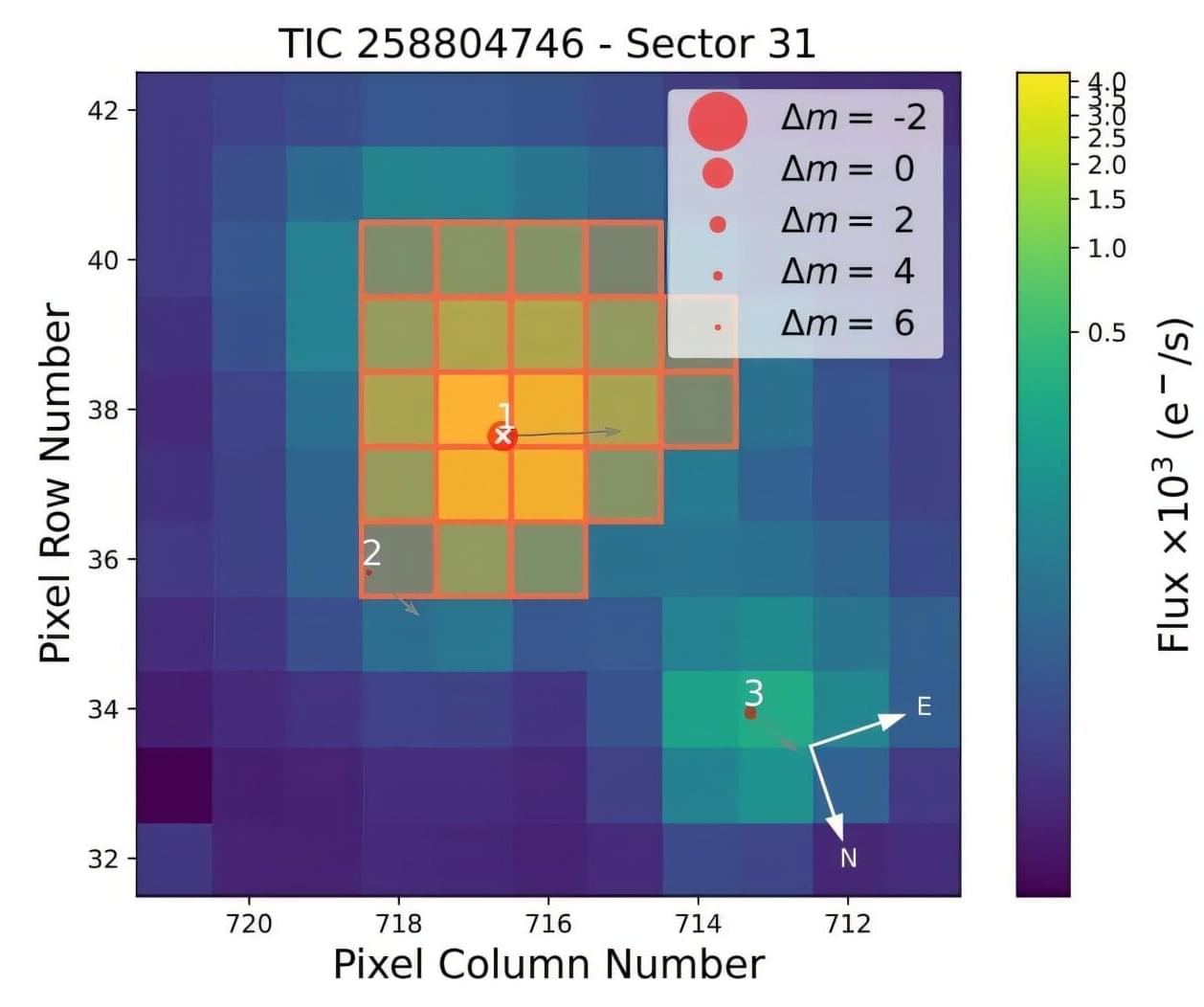
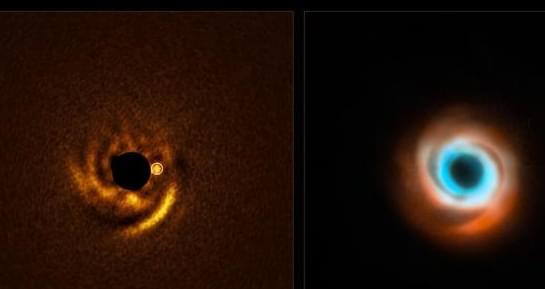
Using the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), an international team of astronomers has detected a new exoplanet orbiting a nearby star. The newfound alien world, designated TOI-2431 b, is comparable in size to Earth and has a very short orbital period. The finding was reported in a research paper published July 11 on the pre-print server arXiv.
NASA’s TESS monitors about 200,000 bright stars near Earth, looking for temporary drops in brightness caused by planetary transits. Since its launch in April 2018, the satellite has identified more than 7,600 candidate exoplanets (TESS Objects of Interest, or TOI), of which 638 have been confirmed so far.
Now, a team of astronomers led by Kaya Han Taş of the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands, reports the confirmation of another TOI monitored by TESS. According to the paper, a transit signal has been detected in the light curve of TOI-2431—a star of spectral type KV7 located some 117 light years away. The planetary nature of this signal was confirmed by follow-up ground-based observations.
Astronomers have just solved a long-standing mystery about a rare, rapidly spinning neutron star known as PSR J1023+0038. Using NASA’s IXPE telescope and a fleet of observatories, scientists discovered that the system’s intense X-rays don’t come from its glowing accretion disk as previously belie
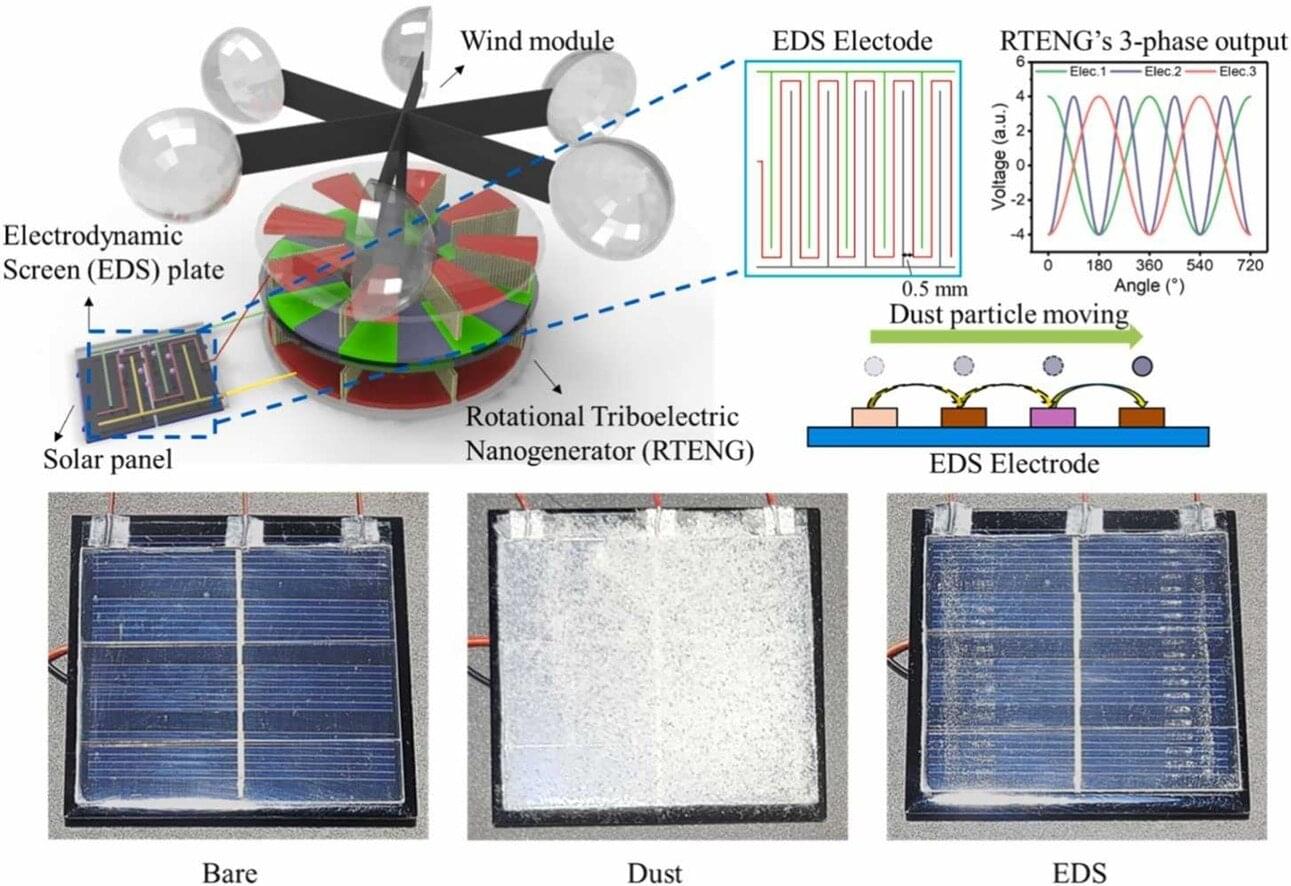
A collaborative research team has successfully developed a self-powered pollution prevention technology that can remove pollutants from the surface of solar panels without external power. This technology uses a wind-powered rotational triboelectric nanogenerator to generate power and combines said power with electrodynamic screen (EDS) technology to move dust in the desired direction for removal.
The findings are published in the journal Nano Energy. The team was led by Professor Juhyuck Lee from the Department of Energy Science and Engineering, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology, along with Dr. Wanchul Seung at Global Technology Research, Samsung Electronics.
The dust that gathers on the surface of solar panels causes a significant reduction in power production efficiency. EDS technology, designed to address this problem, uses electric fields to remove dust from the surface, and it is noted for environments that are not easily accessible, such as deserts, mountains, and space, as it does not require cleaning equipment or personnel. Traditional EDS technology, however, requires high voltage and, consequently, external power, and it has the disadvantage of additional maintenance costs.

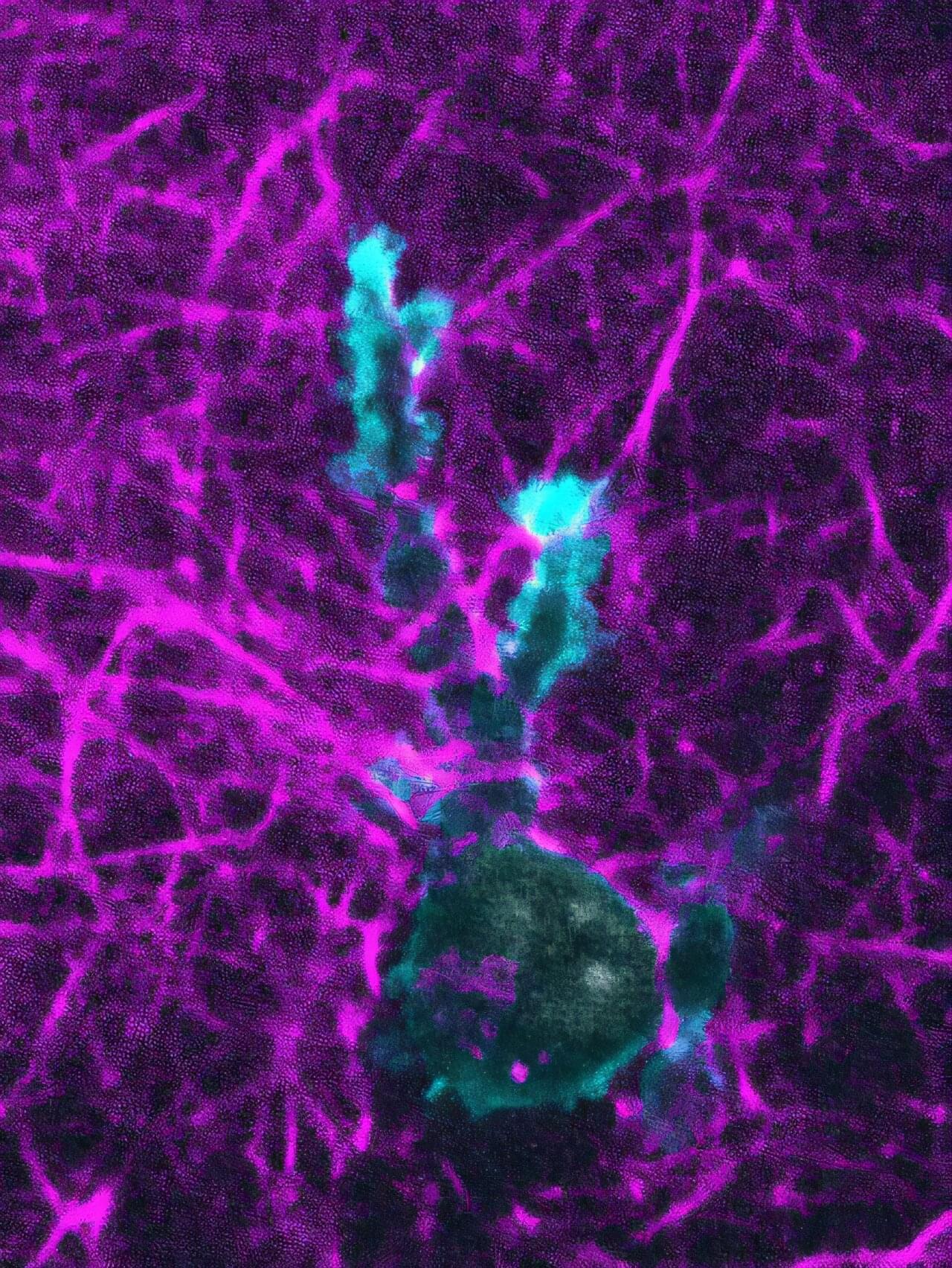
Immune responses rely on the efficient movement of immune cells within the complex and geometrically unpredictable three-dimensional tissues that make up our bodies.
Research by the Sixt group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) unveils how immune cells use their cytoskeleton to exert forces on their surrounding environment to push their way through tissues.
The findings were published in Nature Immunology.