Astronomers studying rare star-forming galaxies reveal how the chaotic past of the universe may mirror the future of the Milky Way.


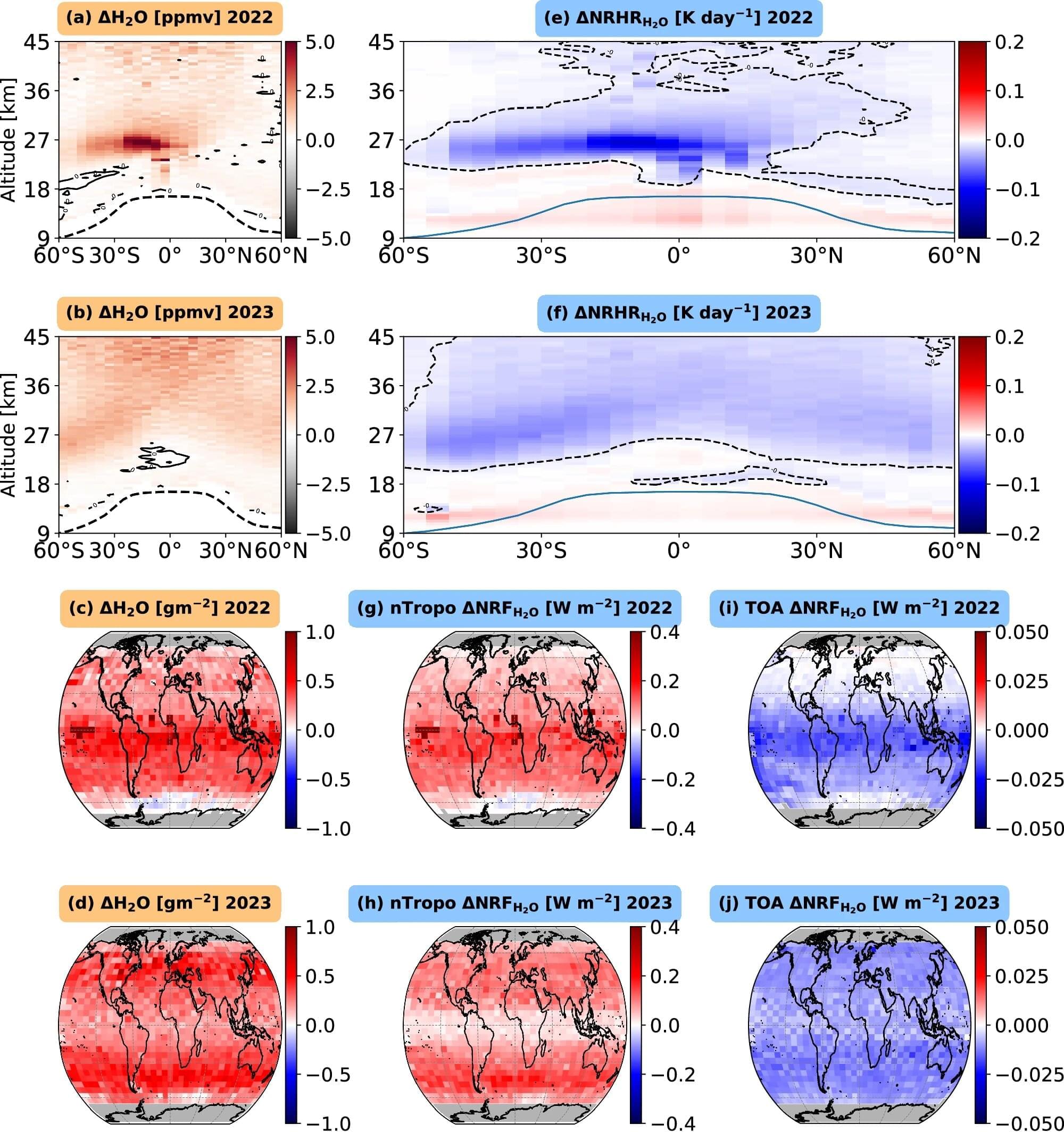
When Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai, an underwater volcano near Tonga in the South Pacific Ocean, erupted in 2022, scientists expected that it would spew enough water vapor into the stratosphere to push global temperatures past the 1.5 C threshold set by the Paris Accords. A new UCLA-led study shows that not only did the eruption not warm the planet, but it actually reduced temperatures over the Southern Hemisphere by 0.1 C.
The reason: The eruption formed smaller sulfate aerosols that had an efficient cooling effect that unexpectedly outweighed the warming effect of the water vapor. Meanwhile, the water vapor interacted with sulfur dioxide and other atmospheric components, including ozone, in ways that did not amplify warming.
While that’s good news, the study also suggests that efforts to reverse climate change by loading the atmosphere with substances that react with solar radiation to send heat back out into space, an effort known as geoengineering, are potentially even riskier than previously thought and must take new complications into account.
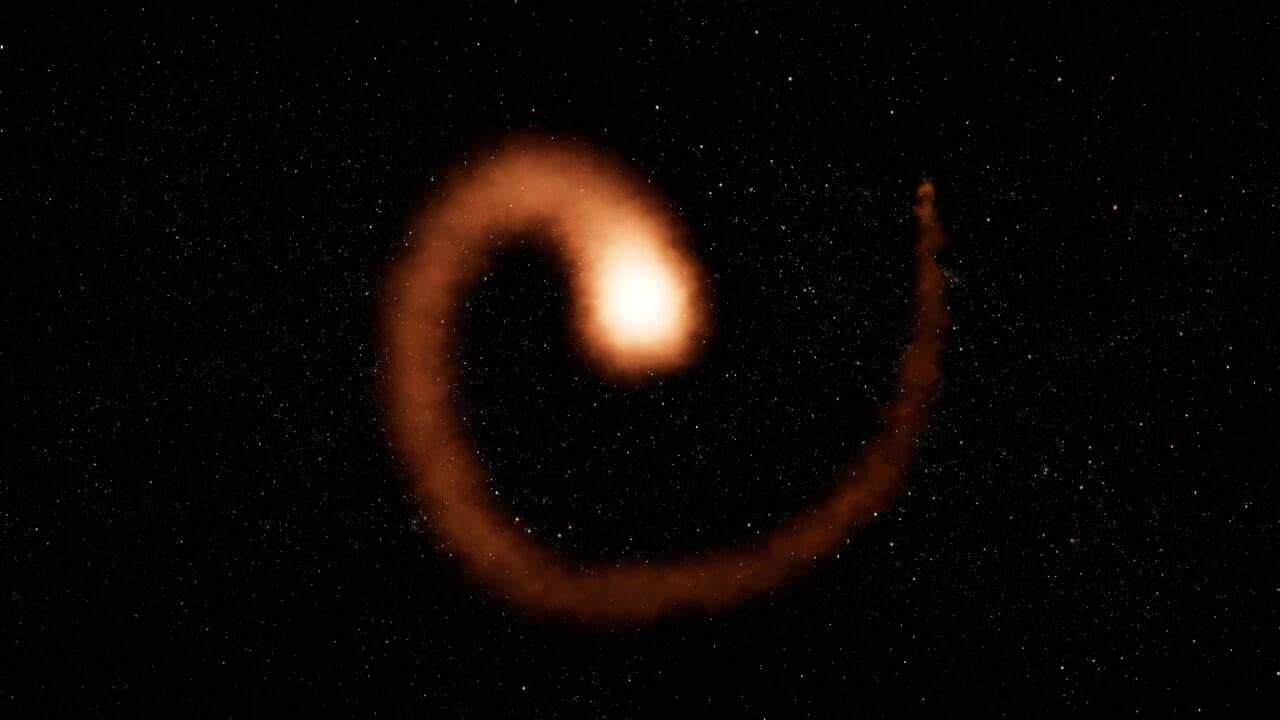

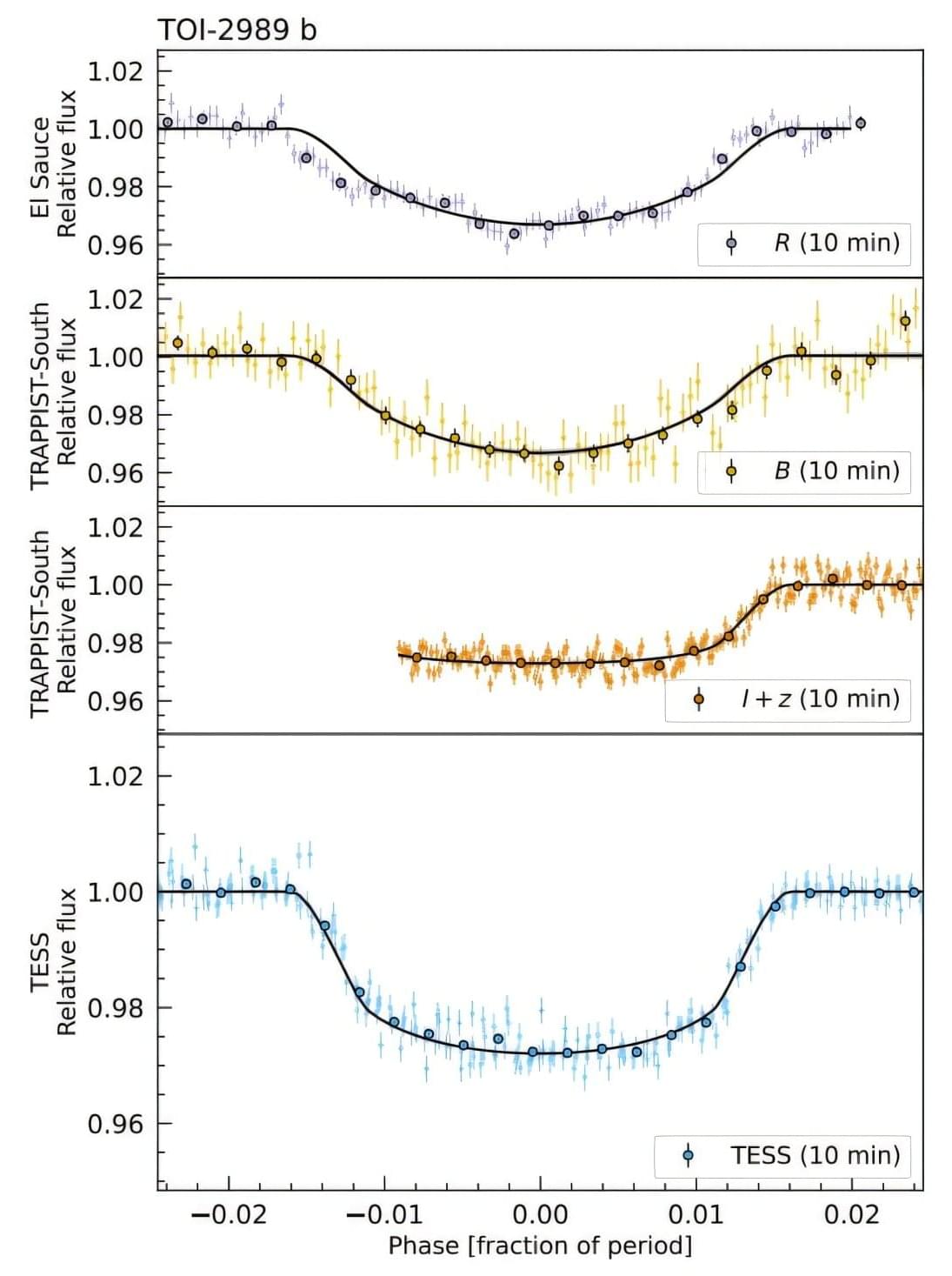
A recent study reveals that the famous Wolf-Rayet 104 “pinwheel star” holds more mystery but is even less likely to be the potential “death star” it was once thought to be.
Research by W. M. Keck Observatory Instrument Scientist and astronomer Grant Hill finally confirms what has been suspected for years: WR 104 has at its heart a pair of massive stars orbiting each other with a period of about 8 months. The collision between their powerful winds gives rise to its rotating pinwheel of dust that glows in the infrared, and spins with the same period.
The pinwheel structure of WR 104 was discovered at Keck Observatory in 1999 and the remarkable images of it turning in the sky astonished astronomers. One of the two stars that were suspected to orbit each other—a Wolf-Rayet star—is a massive, evolved star that produces a powerful wind highly enriched with carbon. The second star—a less evolved but even more massive OB star—has a strong wind that is still mostly hydrogen.
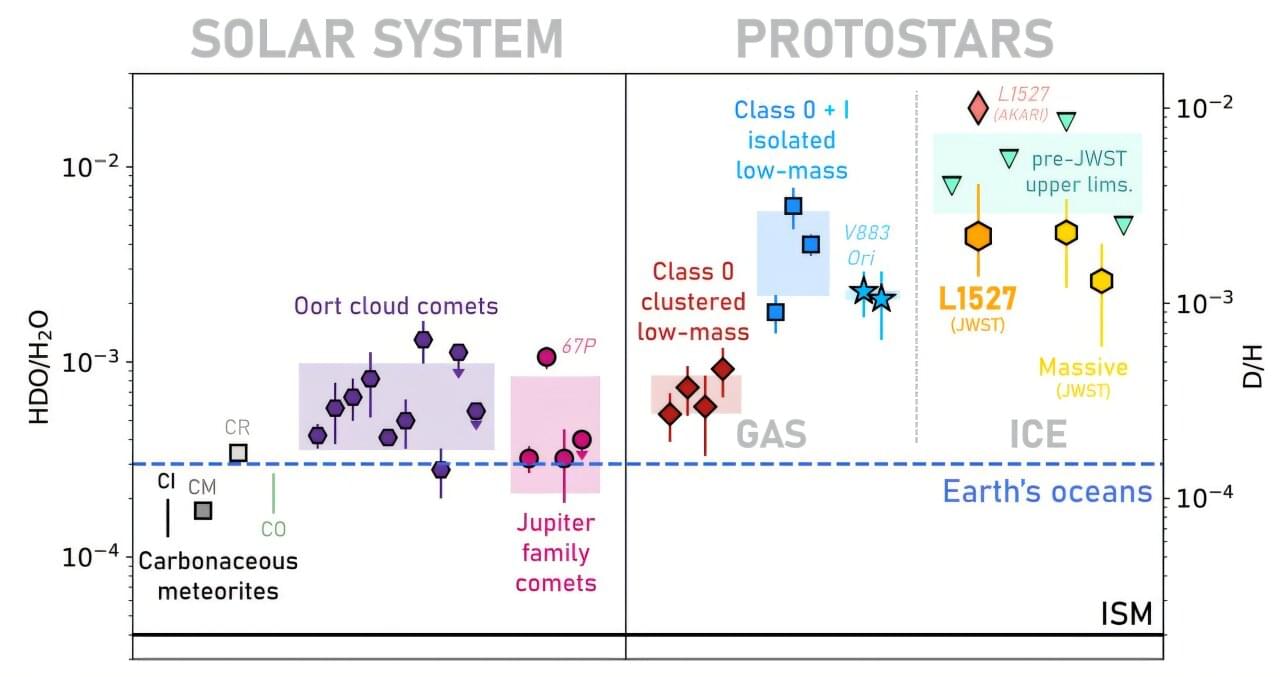
A team led by astronomers at Leiden University in the Netherlands and the National Radio Astronomy Observatory in Virginia (U.S.) have, for the first time, robustly detected semi-heavy water ice around a young sunlike star. The results strengthen the case that some of the water in our solar system formed before our sun and the planets.
Their findings are published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
One way that astronomers trace the origin of water is through measuring its deuteration ratio. That is the fraction of water that contains one deuterium atom instead of one of the hydrogens. So instead of H2O, it’s HDO, which is also called semi-heavy water. A high fraction of semi-heavy water is a sign that the water formed in a very cold place, such as the primitive dark clouds of dust, ice, and gas from which stars are born.
We have long taken it for granted that gravity is one of the basic forces of nature – one of the invisible threads that keeps the universe stitched together. But suppose that this is not true. Suppose the law of gravity is simply an echo of something more fundamental: a byproduct of the universe operating under a computer-like code.
That is the premise of my latest research, published in the journal AIP Advances. It suggests that gravity is not a mysterious force that attracts objects towards one another, but the product of an informational law of nature that I call the second law of infodynamics.
It is a notion that seems like science fiction – but one that is based in physics and evidence that the universe appears to be operating suspiciously like a computer simulation.

Scientists are analysing the smells of space – from the aroma onboard space stations to planets hundreds of light years away – to learn about the makeup of the Universe.
About a century ago, scientists were struggling to reconcile what seemed a contradiction in Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
Published in 1915, and already widely accepted worldwide by physicists and mathematicians, the theory assumed the Universe was static – unchanging, unmoving and immutable. In short, Einstein believed the size and shape of the Universe today was, more or less, the same size and shape it had always been.
But when astronomers looked into the night sky at faraway galaxies with powerful telescopes, they saw hints the Universe was anything but that. These new observations suggested the opposite – that it was, instead, expanding.