The galaxies have never before been captured in such detail.
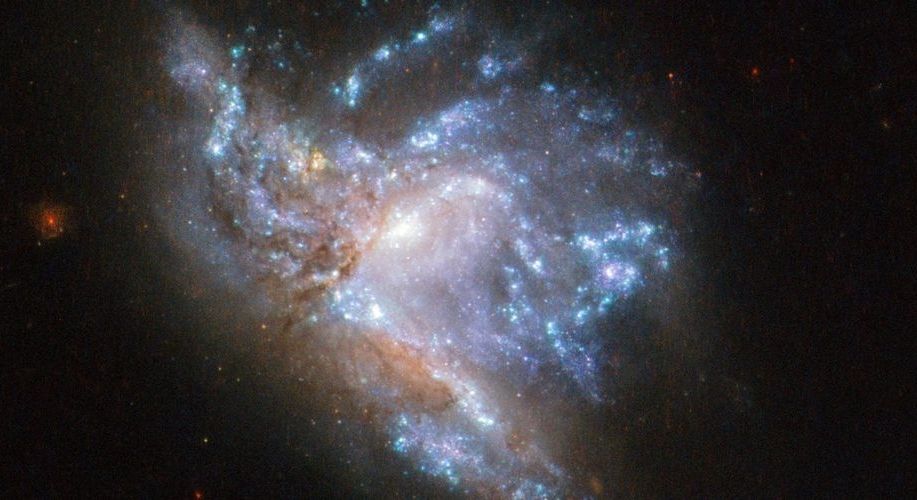
First discovered in 1784 by William Herschel, NGC 6052 was originally thought to be a singular galaxy that simply had an odd shape.
However, scientists eventually figured out that the “oddly shaped galaxy” 230 million light-years away was, in fact, two galaxies in the process of colliding.
Having previously been observed by the Hubble telescope with an older camera in 2015, NASA recently released a stunning image of the galaxies in even better detail.