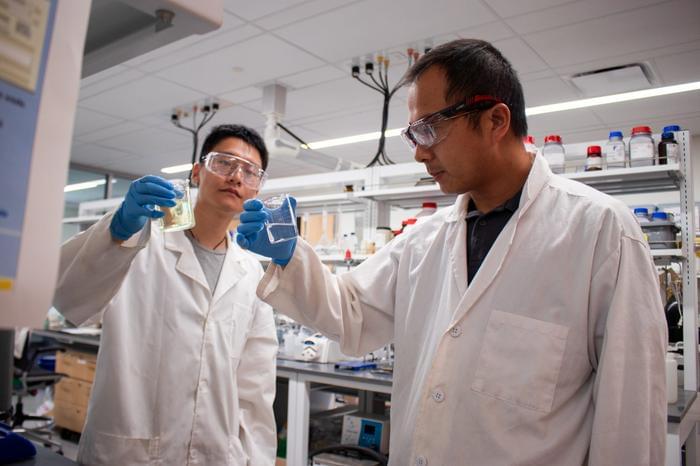
A team led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory identified and successfully demonstrated a new method to process a plant-based material called nanocellulose that reduced energy needs by a whopping 21%. The approach was discovered using molecular simulations run on the lab’s supercomputers, followed by pilot testing and analysis.
The method, leveraging a solvent of sodium hydroxide and urea in water, can significantly lower the production cost of nanocellulosic fiber — a strong, lightweight biomaterial ideal as a composite for 3D-printing structures such as sustainable housing and vehicle assemblies. The findings support the development of a circular bioeconomy in which renewable, biodegradable materials replace petroleum-based resources, decarbonizing the economy and reducing waste.
Colleagues at ORNL, the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, and the University of Maine’s Process Development Center collaborated on the project that targets a more efficient method of producing a highly desirable material. Nanocellulose is a form of the natural polymer cellulose found in plant cell walls that is up to eight times stronger than steel.