TIME got to try the world’s first lab-grown steak, no cows required.



Now, there’s another flying race car concept in the game. French startup Maca Flight revealed a new hydrogen-powered flying race car concept at the 2022 CES and it’s remarkably similar to the podracers in the Star Wars universe.
A green flying race car concept
Called a carcopter, a portmanteau of the words car and helicopter, Maca S11 is designed for speed and sustainability. And unlike others in its class, it’s powered by a hydrogen fuel cell instead of a conventional battery. The company states that the eVTOL is priced at just over $900,000 and that it will be ready to hit the racetrack in 2023.

The business mogul’s opening up to more ‘free speech’ on Twitter may have ruffled some feathers.
Elon Musk might have just hinted at making Tesla phones (Tesla Pi) a reality if Apple and Google were to “boot” Twitter from their app stores.
“If Apple & Google boot Twitter from their app stores, @elonmusk should produce his own smartphone,” Liz Wheeler, a video podcaster, said in a Twitter thread on Friday.
Muhammed selim korkutata / anadolu agency/getty images.
The business mogul’s opening up to more “free speech” on Twitter may have ruffled some feathers, and the tech world is a buzz with rumors surrounding Twitter’s future in the Apple and Google app stores.

The story of the damage done to the world’s biodiversity is a tale of decline spanning thousands of years. Can the world seize its chance to change the narrative?
The story of the biodiversity crisis starts with a cold-case murder mystery that is tens of thousands of years old. When humans started spreading across the globe they discovered a world full of huge, mythical-sounding mammals called “megafauna”, but by the end of the Pleistocene, one by one, these large animals had disappeared. There is no smoking gun and evidence from ancient crime scenes is — unsurprisingly — patchy. But what investigators have learned suggests a prime suspect: humans.

Every year, the EU generates over 2.5 billion tonnes of waste – that’s 5 tonnes per person. The good news is that much of this waste can be recycled and reused. The bad news, however, is that doing so requires proper collection processes, which is often easier said than done.
“The challenge with waste collection is that it is a widely dispersed process,” says Tjerk Wardenaar, a consultant at EGEN, part of the PNO Group, the project’s lead partner. “Individual consumers discard small amounts of waste, local and regional authorities implement collection systems, waste management companies do the actual collecting, recycling companies recover materials, and so on.”
With the support of the EU-funded COLLECTORS project, Wardenaar aims to increase our understanding of how these various steps relate to one another. “Waste collection depends on a combination of social and technical factors,” he explains. “Our goal is to identify best practices that decision makers can use to implement an integrated waste collection system that supports Europe’s transition to a waste-free, circular economy.”
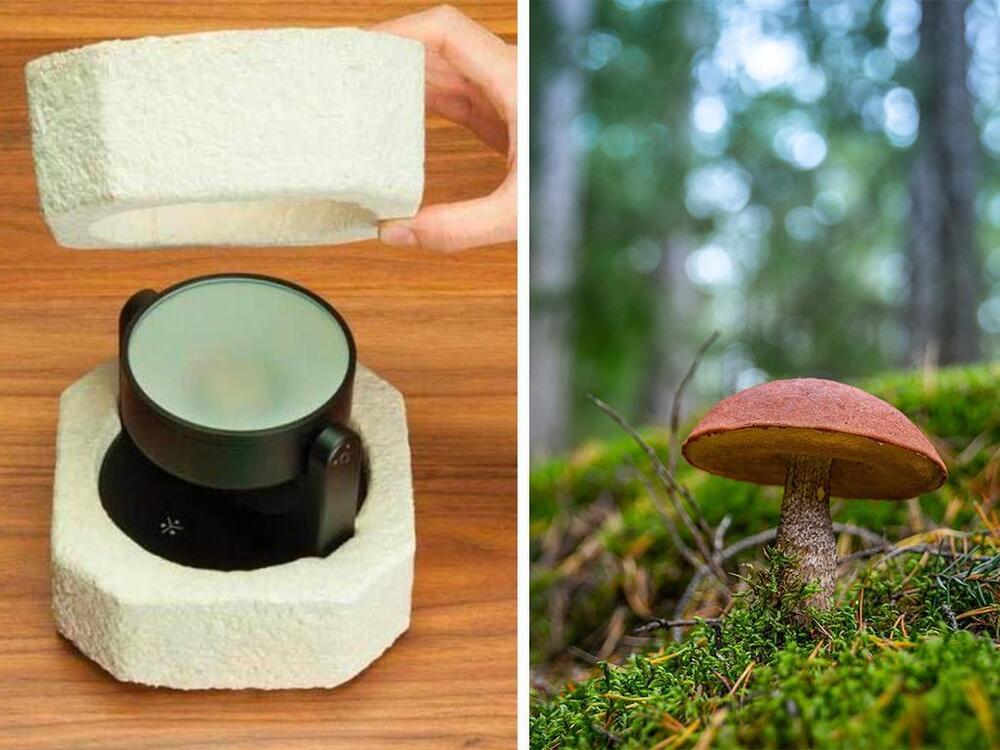

Mushroom-foam is as cheap as Styrofoam, requires no fossil fuel, and creates no plastic pollution, biodegrading in your garden in just a couple of weeks Ikea is switching to a new mushroom-based, biodegradable alternative to polystyrene (Styrofoam) packaging for its furniture and home decor. Known as Mycofoam, the product is […].
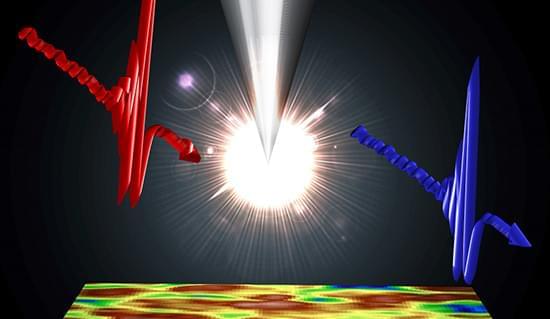
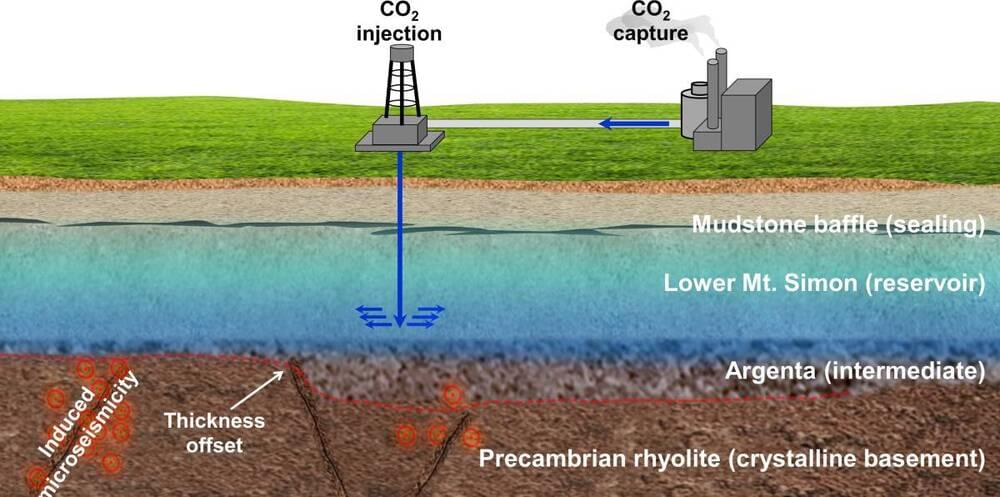
Mitigating and reversing the effects of climate change is the most important scientific challenge facing humanity. Carbon sequestration describes a range of technologies with the potential to reduce the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere. Most of these schemes involve storing the gas underground, however, this is not without risk, and scientists are concerned that underground storage could lead to increased seismic activity (a phenomenon known as “induced seismicity”).
Now, researchers in the US and Switzerland have studied microseismicity, the small seismic events caused by carbon injection into host rock, at the Illinois Basin Decatur Project (IBDP) in the midwestern US. In 2011–2014, the IBDP injected one million tonnes of CO2 into an underground reservoir just above a rhyolite crystalline basin. Nikita Bondarenko and Roman Makhnenko at the University of Illinois and Yury Podladchikov at the University of Lausanne have used a combination of field observations and computer simulations to show how microseismicity at the IBDP is highly dependent on the microscale structure of the host rock.
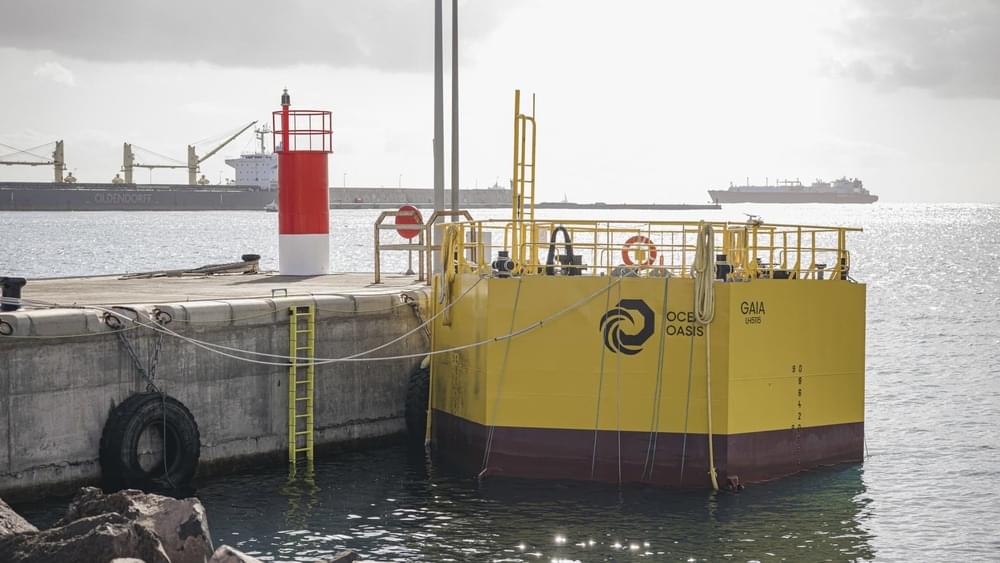

With the above in mind, projects looking to desalinate water in a more sustainable way will become increasingly important in the years ahead.
The idea of using waves to power desalination is not unique to the project being undertaken in the Canaries. In April, for example, the U.S. Department of Energy revealed the winners of the last stage of a competition focused on wave-powered desalination.
Back on the Canary Islands, Ocean Oasis said it would be looking to construct a second installation after testing at the PLOCAN facility had taken place. “In this phase, the prototype will be scaled with the capacity to produce water for consumption,” the company said.

One of Tesla’s upcoming software updates should give the sound systems in its current and new vehicles a considerable upgrade. According to our source, Tesla has been working with major record labels for months to bring Dolby Atmos to Tesla cars. Once the software update rolls out, over 1 million Teslas that are currently on the road will support Dolby Atmos, including all newly manufactured vehicles.
Dolby Atmos is a surround sound format from Dolby that uses height channels to interpret sounds as 3D objects. Dolby Atmos debuted in 2012 in Los Angeles, and has since made its way into thousands of movie theaters, home theaters, and even cars.
Lucid Motors was the first carmaker to bring Dolby Atmos sound to its Lucid Air sedan early last year. This fall, Volvo and Mercedes-Benz revealed that they will be bringing Dolby Atmos to more cars as well. Volvo’s EX90 SUV will have Dolby Atmos, while Mercedes-Benz is adding Atmos to the Mercedes-Maybach S-Class, Mercedes-Benz S-Class, and its EQE, EQE SUV, EQS, and EQS SUV electric vehicles. Before long, Tesla should be on this list, too.