This could make electric cars as affordable as combustion engine vehicles.
Tesla says it can dramatically reduce the price for electric cars. Tesla CEO Elon Musk made the announcement during the company’s “Battery Day” for investors.
This could make electric cars as affordable as combustion engine vehicles.
Tesla says it can dramatically reduce the price for electric cars. Tesla CEO Elon Musk made the announcement during the company’s “Battery Day” for investors.

Featured image: @Carroll__Burns/Twitter
At the Q2 2020 Earnings Call, Tesla CEO Elon Musk announced the location of the new factory. The Gigafactory for the production of the Semi, Cybertruck, Model Y, and Model 3 will be built in Austin, Texas and will be Tesla’s largest factory yet.
For now, the plan describes a 280-acre building, although the company has purchased a 2,100-acre site. Of course, given the company’s plans for the production of the Semi, Cybertruck, Model Y, and Model 3—as well as the presence of a recreation area on the territory of Giga Texas—it is not surprising that Tesla needs such a massive piece of land.
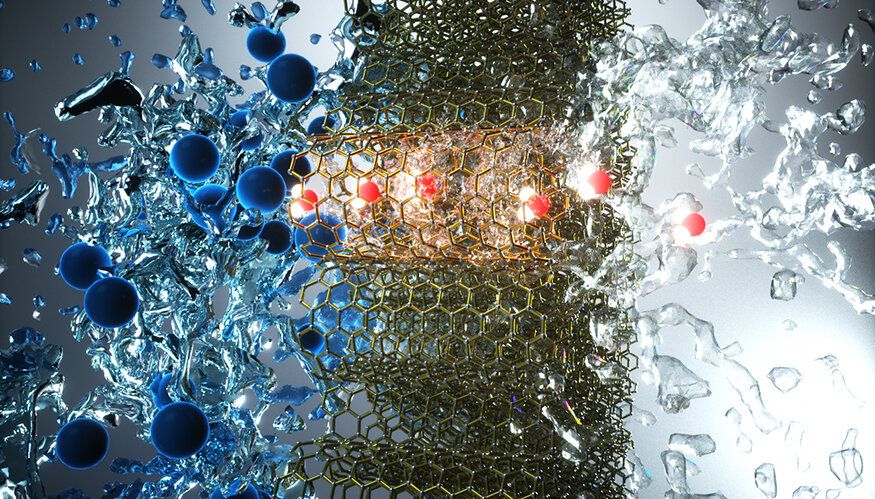
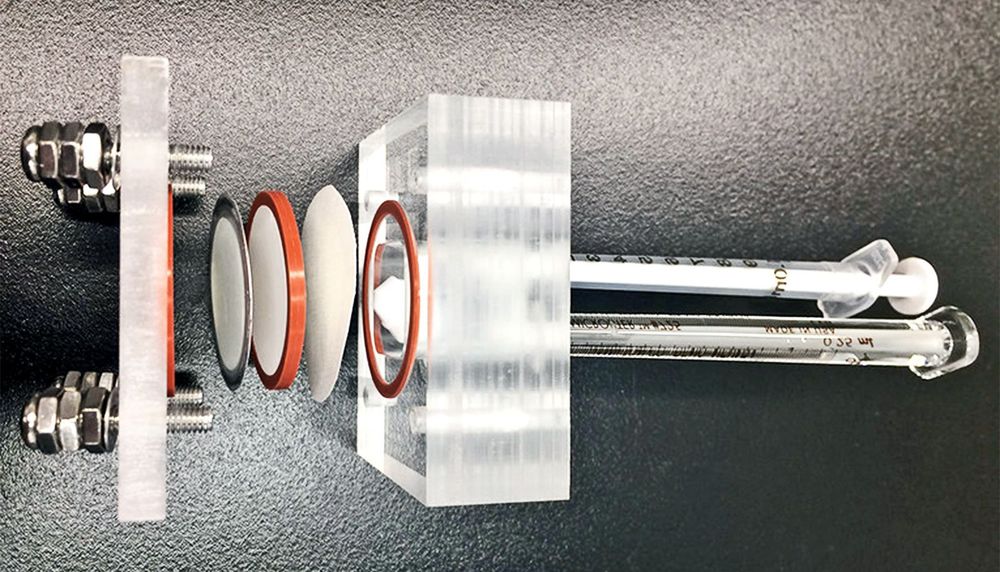
Membrane separations have become critical to human existence, with no better example than water purification. As water scarcity becomes more common and communities start running out of cheap available water, they need to supplement their supplies with desalinated water from seawater and brackish water sources.
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have created carbon nanotube (CNT) pores that are so efficient at removing salt from water that they are comparable to commercial desalination membranes. These tiny pores are just 0.8 nanometers (nm) in diameter. In comparison, a human hair is 60,000 nm across. The research appears on the cover of the Sept. 18 issue of the journal Science Advances.
The dominant technology for removing salt from water, reverse osmosis, uses thin-film composite (TFC) membranes to separate water from the ions present in saline feed streams. However, some fundamental performance issues remain. For example, TFC membranes are constrained by the permeability-selectivity trade-offs and often have insufficient rejection of some ions and trace micropollutants, requiring additional purification stages that increase the energy and cost.
A new type of battery has been developed that could revolutionise electric vehicle use with a recharge time of just 15 seconds.

Just in case you haven’t heard, Long Way Up is the third installment in Ewan McGregor’s and Charlie Boorman’s trilogy of long-distance motorcycle adventure rides.
What makes this one so special, though, is that the duo set out on a pair of Harley-Davidson LiveWire electric motorcycles, attempting to cover 15,000 miles (25,000 km) of incredibly remote terrain from the southern tip of Argentina all the way to Los Angeles.
[Author’s Note: There are no major spoilers here; you’re safe to keep reading.].
World hunger is a persistent problem despite all of humanity’s progress in recent years. However, I believe that we have a real shot at defeating world hunger with one of humanity’s newer innovations: vertical farms.
Discord Link: https://discord.gg/brYJDEr
Patreon link: https://www.patreon.com/TheFuturistTom
Please follow our instagram at: https://www.instagram.com/the_futurist_tom
For business inquires, please contact [email protected]

CIEQSFTTLFACQTAAEIWRAFGYTVKIMVDNGNCRLHVC: these forty letters are a set of instructions for building a sophisticated medical device designed to recognize the flu virus in your body. The device latches onto the virus and deactivates the part of it that breaks into your cells. It is impossibly tiny—smaller than the virus on which it operates—and it can be manufactured, in tremendous quantities, by your own cells. It’s a protein.
Proteins—molecular machines capable of building, transforming, and interacting with other molecules—do most of the work of life. Antibodies, which defend our cells against invaders, are proteins. So are hormones, which deliver messages within us; enzymes, which carry out the chemical reactions we need to generate energy; and the myosin in our muscles, which contract when we move. A protein is a large molecule built from smaller molecules called amino acids. Our bodies use twenty amino acids to create proteins; our cells chain them together, following instructions in our DNA. (Each letter in a protein’s formula represents an amino acid: the first two in the flu-targeting protein above are cysteine and isoleucine.) After they’re assembled, these long chains crumple up into what often look like random globs. But the seeming chaos in their collapse is actually highly choreographed. Identical strings of amino acids almost always “fold” into identical three-dimensional shapes. This reliability allows each cell to create, on demand, its own suite of purpose-built biological tools. “Proteins are the most sophisticated molecules in the known universe,” Neil King, a biochemist at the University of Washington’s Institute for Protein Design (I.P.D.), told me. In their efficiency, refinement, and subtlety, they surpass pretty much anything that human beings can build.
Today, biochemists engineer proteins to fight infections, produce biofuels, and improve food stability. Usually, they tweak formulas that nature has already discovered, often by evolving new versions of naturally occurring proteins in their labs. But “de novo” protein design—design from scratch—has been “the holy grail of protein science for many decades,” Sarel Fleishman, a biochemist at the Weizmann Institute of Science, in Israel, told me. Designer proteins could help us cure diseases; build new kinds of materials and electronics; clean up the environment; create and transform life itself. In 2018, Frances Arnold, a chemical engineer at the California Institute of Technology, shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for her work on protein design. In April, when the coronavirus pandemic was peaking on the coasts, we spoke over video chat. Arnold, framed by palm trees, sat outside her home, in sunny Southern California. I asked how she thought about the potential of protein design. “Well, I think you just have to look at the world behind me, right?” she said. “Nature, for billions of years, has figured out how to extract resources from the environment—sunlight, carbon dioxide—and convert those into remarkable, living, functioning machines. That’s what we want to do—and do it sustainably, right? Do it in a way that life can go on.”
