Another interesting aspect of The North Face’s latest fabric tech is that it developed it with sustainability in mind. The company said that every Futurelight garment will be produced at a solar-powered factory, and they’ll be made from recycled materials and will go through a process that cuts chemical consumption. In other words, not only are waterproof, lightweight and comfortable, but they’re good for the environment, as well. (Or at least, not as bad as a lot of other synthetic fabrics.)
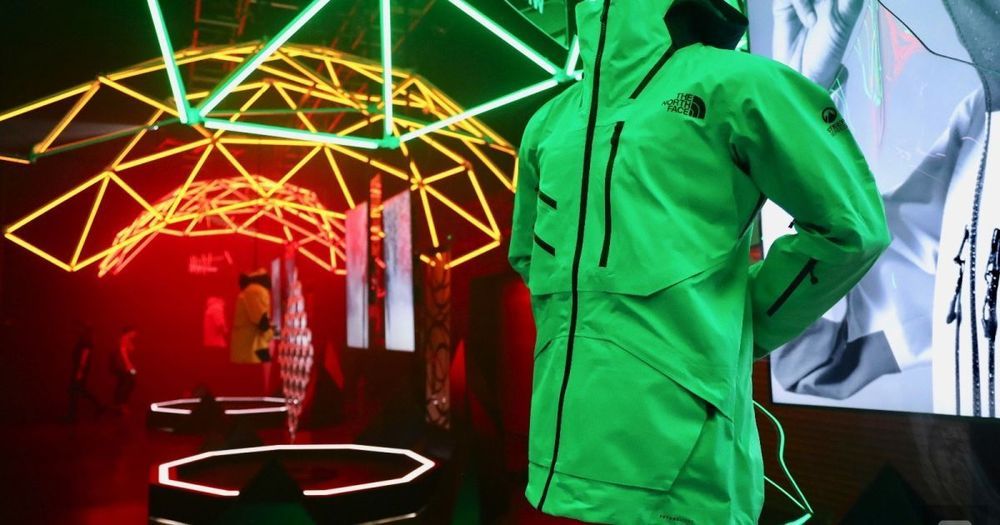
To celebrate the launch of Futurelight, The North Face built an elaborate art installation in New York City. In it, you could see its new high-tech jackets floating underneath thinly disguised marketing messages like, “WHAT IF WATERPROOF GEAR KEPT YOU DRY INSIDE AND OUT?” and “WHAT IF BREATHABILITY IS THE BREAKTHROUGH.” There was also a giant triangle displaying images of snow-covered mountains and other outdoor scenes. Of course, it was all relevant to what The North Face is known for: making clothes for adventurous people.
The North Face’s Futurelight jacket collection is available now on its site, with the men’s Flight Series jackets starting at a cool $280. And, eventually, The North Face plans to put the technology in other gear, including tents, gloves and more.