At this year’s London Marathon, runners tested out algae pods filled with water instead of paper cups. Algae is the newest sustainable trend.



Here is a vegetable weeding robot designed to increase efficiency on large-scale vegetable farms. It works autonomously and can cover up to 12 acres in 9 hours. It uses GPS and camera to get the job done with accuracy.

Dino is designed to reduce labor costs and free up time for farming teams to focus on more important tasks. It can be put on a schedule and since it’s electric, only minimal maintenance is required.
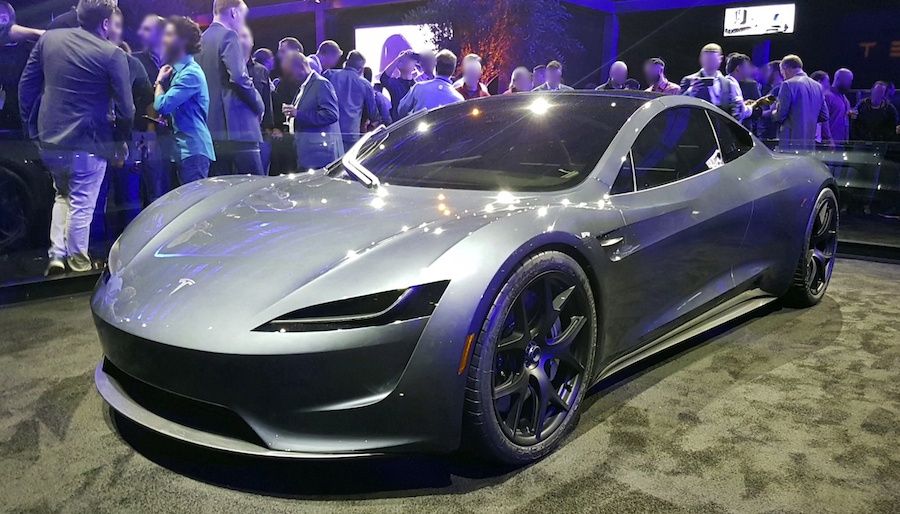

The previous Tesla Roadster Battery range of 1000 km was a conservative estimate. It is the range which users will get if they drive like a maniac. Who can blame them, when the car does 0–100 km/h in under 2 seconds.
Furthermore, Tesla fans also remember that a founders edition with cold gas thrusters is also coming in very limited numbers for hardcore electric car enthusiasts.
It is 2019 and the numbers provided by electric cars have already begun to eclipse the likes of Lamborghini Aventador and Bugatti Veyron. Lamborghini Aventador currently gives 10 MPG (Miles per gallon) or 4.25 km/l in the city, while the Bugatti Veyron delivers an embarrassingly low 7 MPG or 2.97 km/l.

ALLENDALE, Mich. (WOOD) — West Michigan scouts gathered Saturday at the Consumers Energy’s Solar Garden in Allendale to learn about sustainability and how they can be good stewards of the earth.
At the event, the scouts learned how their choices have an impact on the environment.
“The sustainability merit badge is actually quite a tough one to do, it requires a lot of thinking, a lot of planning,” said John Miller, Western Michigan University professor and merit badge counselor. “That’s part of what scouting is about is having the youth learn that they can effect change.”

Just as the modern computer transformed our relationship with bits and information, AI will redefine and revolutionize our relationship with molecules and materials. AI is currently being used to discover new materials for clean-tech innovations, such as solar panels, batteries, and devices that can now conduct artificial photosynthesis.
Today, it takes about 15 to 20 years to create a single new material, according to industry experts. But as AI design systems skyrocket in capacity, these will vastly accelerate the materials discovery process, allowing us to address pressing issues like climate change at record rates. Companies like Kebotix are already on their way to streamlining the creation of chemistries and materials at the click of a button.
Atomically precise manufacturing will enable us to produce the previously unimaginable.
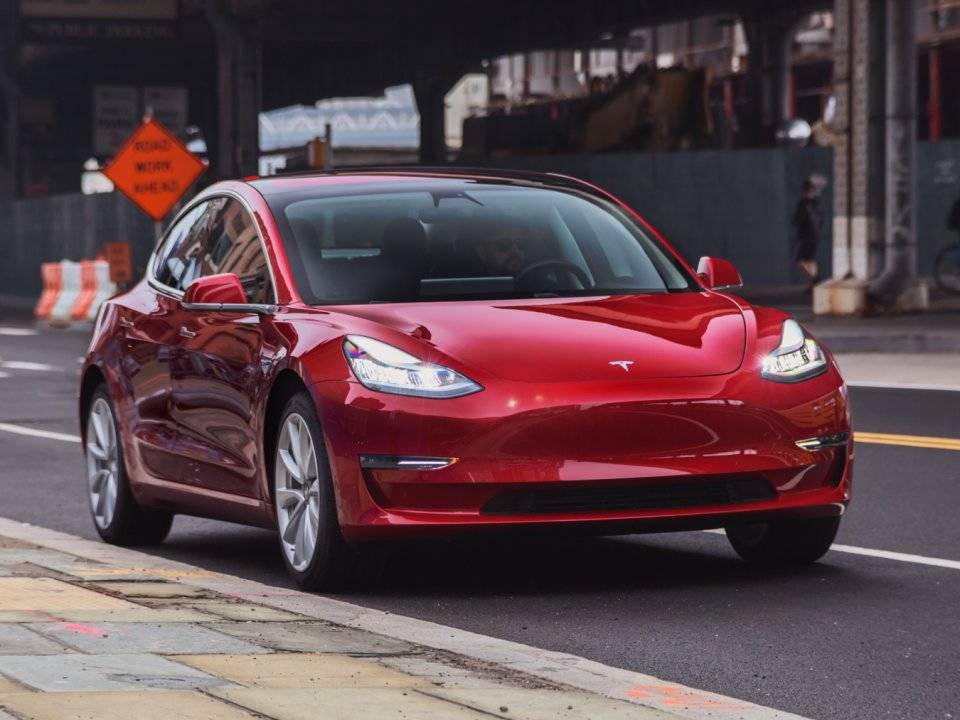

Tesla has begun delivering the $35,000, base-priced version of its Model 3 sedan, three customers have told Business Insider. Electrek first reported on April 15 that Tesla had started delivering the $35,000 Model 3, known as the standard-range trim.
The beginning of standard-range Model 3 deliveries is a landmark for Tesla, but the electric-car maker has been unusually quiet about it. While Tesla posted on its website and social media accounts when it began allowing customers to order the standard-range trim in February, the company has only made reference to the beginning of deliveries near the bottom of an April 11 blog post about an update to its product offerings.
Innolith AG, Swiss maker of rechargeable Inorganic Battery Technology, says they have the world’s first 1000 Wh/kg rechargeable battery. This would triple the range of electric cars. The Innolith Energy Battery would radically reduce costs by not using exotic and expensive materials.
Innolith will make an initial pilot production in Germany and then create licensing partnerships with major battery and automotive companies. Development and commercialization of the Innolith Energy Battery is anticipated to take between three and five years.
It will also be the first non-flammable lithium-based battery for use in EVs. The Innolith battery uses a non-flammable inorganic electrolyte, unlike conventional EV batteries that use a flammable organic electrolyte. The switch to non-flammable batteries removes the primary cause of battery fires that have beset the manufacturers of EVs.
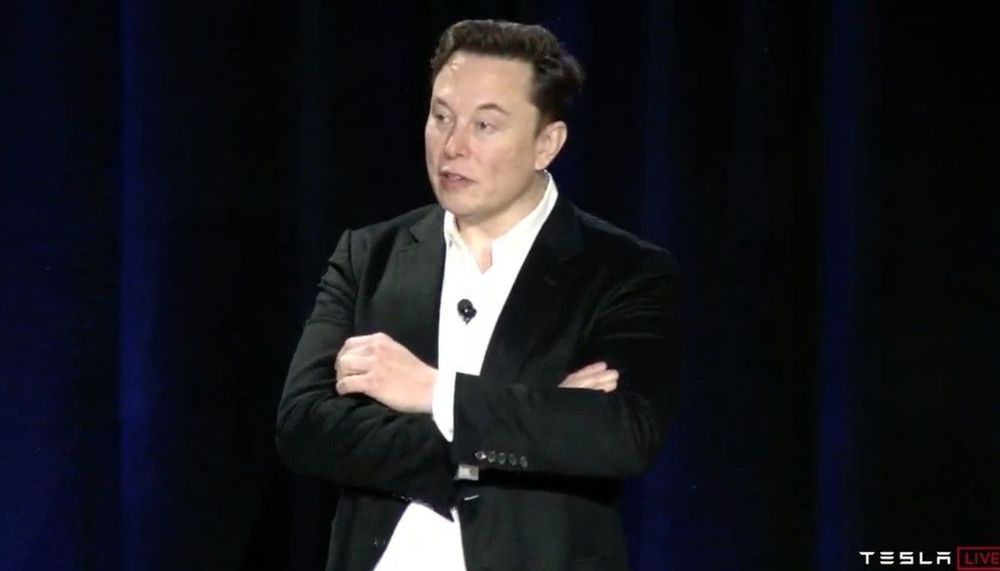

Elon Musk has tweeted that Tesla will make a quiet electric leaf blower.
In 2017, the California Air Resources Board, said that by 2020, the biggest single ozone polluter in California is going to be all this gardening equipment.
California has 16 million gas-powered garden machines from leaf blowers to mowers.
Two years ago a team of scientists visited Costa Rica’s subduction zone, where the ocean floor sinks beneath the continent and volcanoes tower above the surface. They wanted to find out if microbes can affect the cycle of carbon moving from Earth’s surface into the deep interior. According to their new study in Nature, the answer is affirmatively—yes they can.
This groundbreaking study shows that microbes consume and—crucially—help trap a small amount of sinking carbon in this zone. This finding has important implications for understanding Earth’s fundamental processes and for revealing how nature can potentially help mitigate climate change.
At a subduction zone there is communication between Earth’s surface and interior. Two plates collide and the denser plate sinks, transporting material from the surface into Earth’s interior. Showing that the microbes at the near-surface are playing a fundamental role in how carbon and other elements are being locked up into the crust provides a profound new understanding of Earth processes and helps researchers model how Earth’s interior may develop over time.
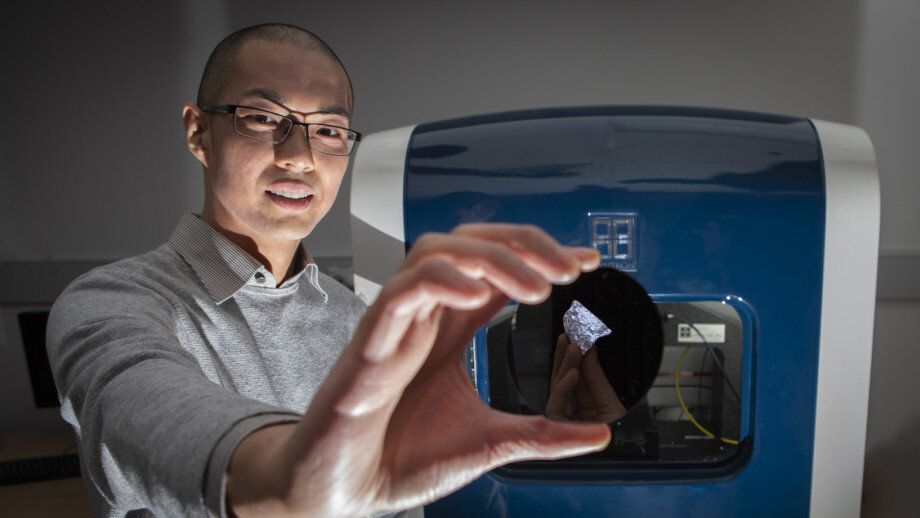
An international research team led by The Australian National University (ANU) has made a new type of silicon that better uses sunlight and promises to cut the cost of solar technology.
The researchers say their world-first invention could help reduce the costs of renewable electricity below that of existing coal power stations, as well as lead to more efficient solar cells.
Senior researcher ANU Professor Jodie Bradby said silicon was used as the raw material for solar cells because of its abundance, low-cost and non-toxicity.