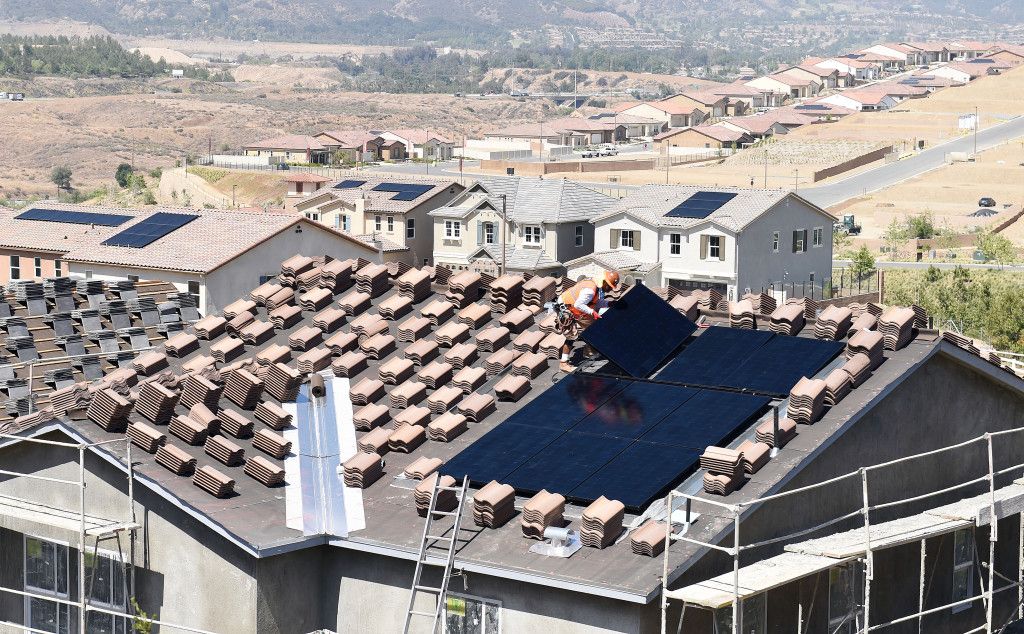
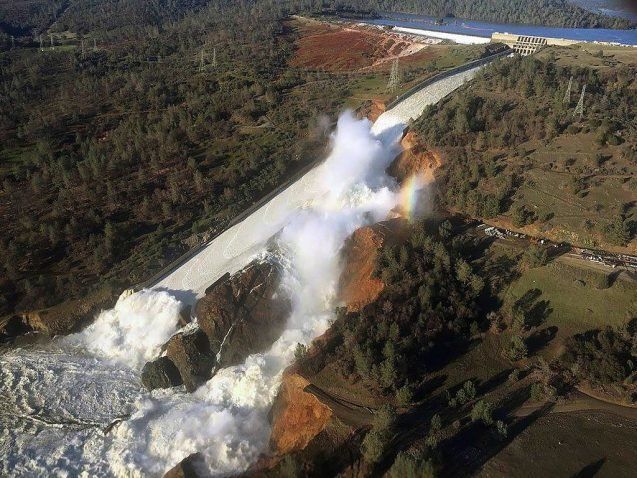
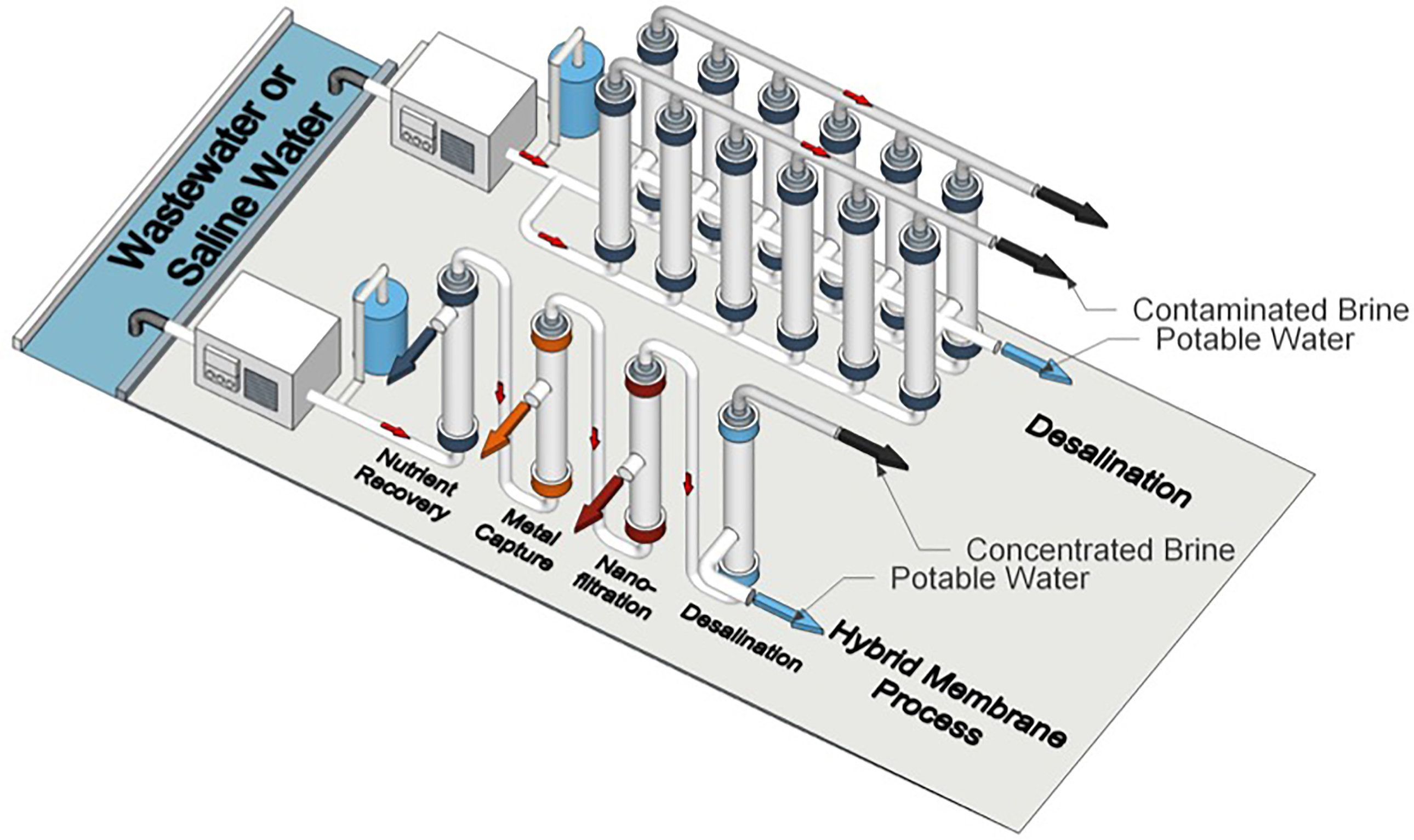
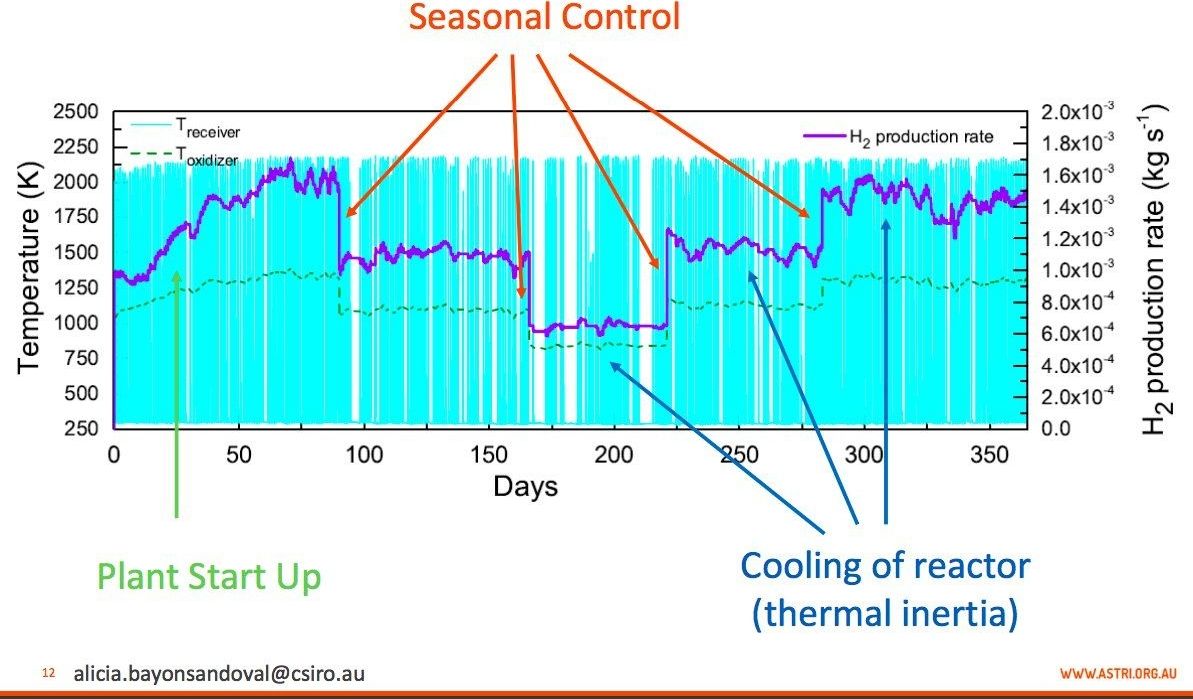
America’s water is under threat from many sides. It faces pollution problems, outdated infrastructure, rising costs, and unprecedented droughts and rainfall patterns as the climate changes. Yet at a recent event hosted by the Columbia Water Center, the tone was cautiously optimistic, and the conversation centered on solutions.
“If we have aging infrastructure that’s falling apart, and we’re dealing with climate variability and change, isn’t that a good opportunity to actually do something?” suggested Upmanu Lall, director of the Columbia Water Center.
For decades, the U.S. has been a leader in water management. Now we’re falling behind; in the latest infrastructure report card, dams, drinking water and wastewater all received D ratings. But Lall thinks the country could get an A. Here are some of the solutions, presented at the event, that could help to get us there.