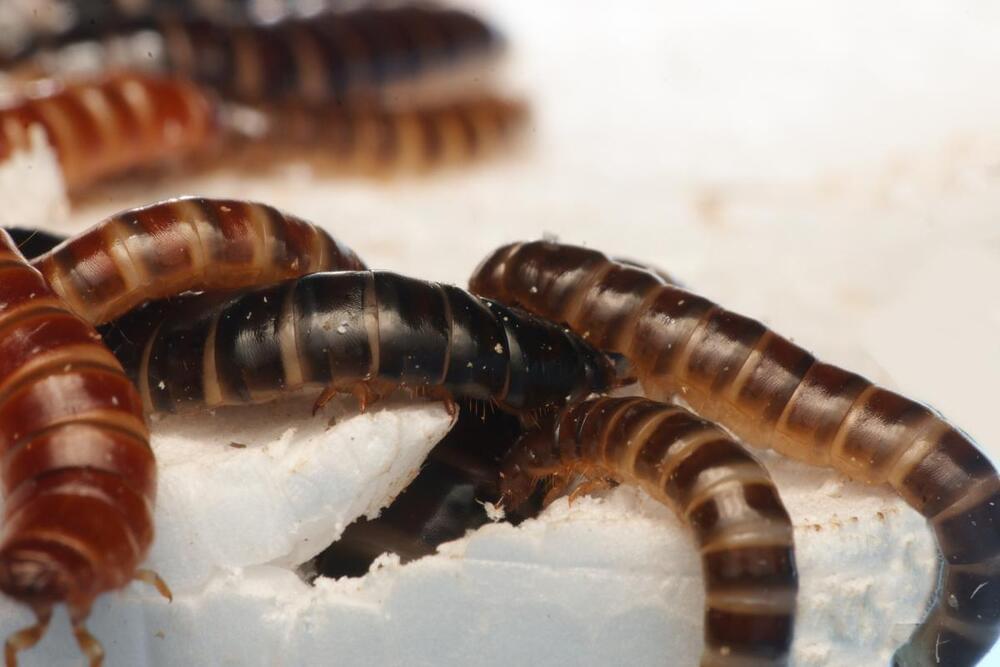
In a paper published in Scientific Reports journal, the researchers report the potential of the lesser mealworm (the larvae of a darkling beetle species, known scientifically as Alphitobius), to consume plastic.
The icipe researchers tested the ability of the lesser mealworm to consume polystyrene, one of the major microplastics that is fast accumulating both in land and water bodies. Polystyrene waste comes from the commercial application of its most common form, styrofoam. This material is used in food storage containers, packaging of equipment, disposable plates and cups, and insulation in construction. Various methods, including chemical, thermal and mechanical, are used to recycle polystyrene. However, these approaches are expensive and they also produce toxic compounds that are harmful to human, environment and biodiversity.
“Our study showed that the mealworms can ingest close to 50% of the styrofoam. We aim to conduct further studies to understand the process through which mealworms consume polystyrene, and whether they gain any nutritional benefits from the material,” says Evalyne Ndotono, an icipe PhD scholar.
“We will also explore the mechanisms of the bacteria in the lesser mealworm in the degradation of plastic. We want to understand if the bacteria are inherent in the mealworms, or if they are a defence strategy acquired after feeding on plastic.”
Additionally, the scientists will research the ability of the lesser mealworm to degrade diverse types of plastics and to convert it into useful, safe products.