Researchers at McGill University have made a significant advance in the development of all-solid-state lithium batteries, which are being pursued as the next step in electric vehicle (EV) battery technology.
By addressing a long-standing issue with battery performance, this innovation could pave the way for safer, longer-lasting EVs. The findings are published in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science.
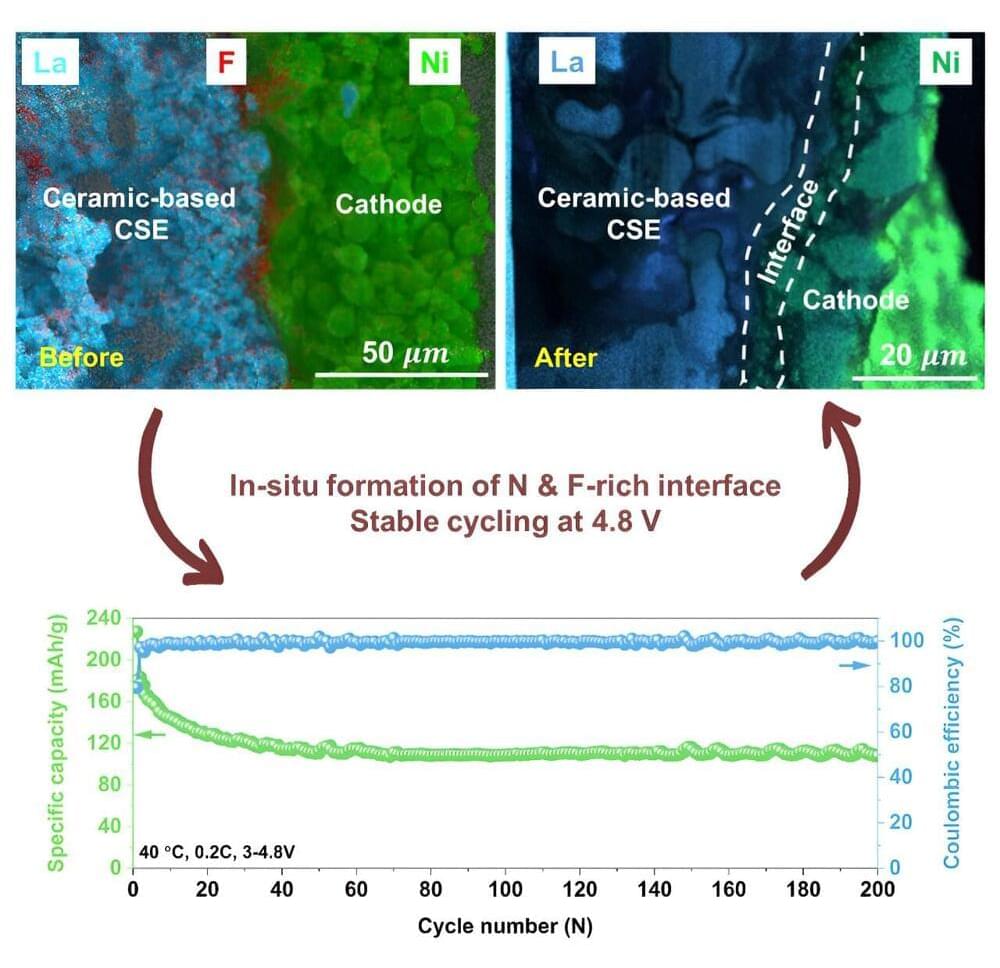
The challenge lies in the resistance that occurs where the ceramic electrolyte meets the electrodes. This makes the battery less efficient and reduces how much energy it can deliver. The research team has discovered that creating a porous ceramic membrane, instead of the traditional dense plate, and filling it with a small amount of polymer can resolve this issue.