My debate on #BasicIncome at the FreedomFest against Dr. Barbara Kolm, director at the Austrian Economic Center (debate moderated by syndicated columnist and scholar Veronique de Rugy) got a write-up in Nevada Current (article by journalist Jeniffer Solis). https://www.nevadacurrent.com/…/universal-basic-income-tou…/ #FFest18
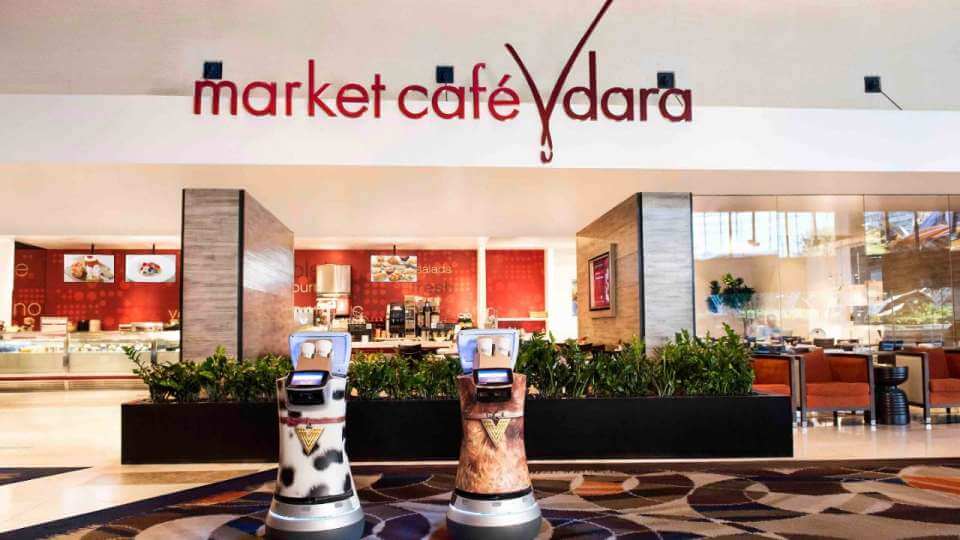
Earlier this month, the Vdara Hotel & Spa added two relay robots that deliver snacks, sundries and spa products directly to guest suites. While charmingly decorated as a Golden Retriever and Dalmatian dog with Vdara-themed collars, the new robots — named Fetch and Jett — may be a sign of what’s next for Las Vegas.
In 20 years, about 65 percent of the city’s jobs could be automated, according to a study by the Institute for Spatial Economic Analysis. That projection may be an outlier – the Organization for Economic for Cooperation and Development, for instance, projects only 10 percent of U.S. jobs are vulnerable to automation.
Still, the highest areas of employment in Las Vegas are in low-skilled service positions like office and administrative support, retail sales, food preparation and serving related occupations — repetitive and routine tasks ripe for automation.
This isn’t news to employees. When contracts between the Culinary and Bartenders unions and many large hospitality companies expired earlier this year, protections against automation were among the topics negotiated in the new five-year contracts.