Great for a spaceship?
It cleans the air five times as efficiently as normal plants.


Uppsala University researchers have devised a new model for the universe – one that may solve the enigma of dark energy. Their new article, published in Physical Review Letters, proposes a new structural concept, including dark energy, for a universe that rides on an expanding bubble in an additional dimension.
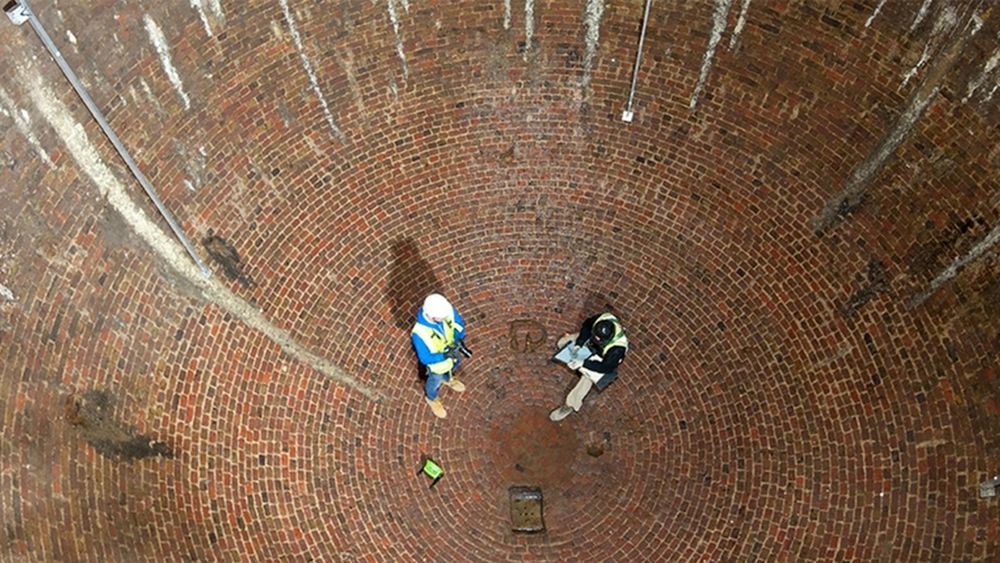

Archaeologists in London have re-discovered a subterranean ice house near Regent’s Park. Dating back to the 1780s, the egg-shaped cavern was used to store ice, which was imported from as far away as Norway.
Made from brick, the structure would have been one of the largest of its kind at the time, according to the Museum of London Archaeology (MOLA). The egg-shaped chamber measures 25 feet (7.5 meters) wide and 31 feet (9.5 meters) deep. Archaeologists with MOLA found the ice house, also known as an ice well, along with its entrance chamber and vaulted ante-chamber, during preparations for the development of the Regent’s Crescent residential project.

Quadcopters with thermal imagery cameras can help detect vicious mini-mines that often kill or maim children.

Their pilot system absorbs excess nutrients, sequesters carbon dioxide and re-oxygenates the water, all while producing an efficient form of energy.
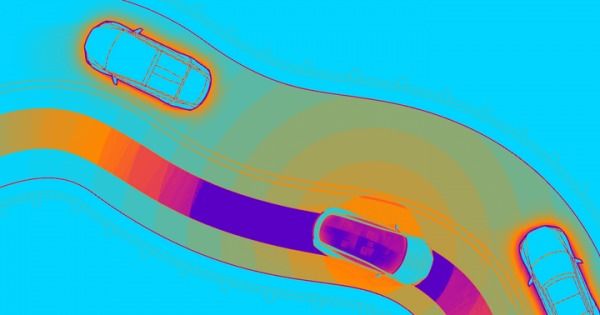
The evidence that self-driving vehicle manufacturers aren’t always upfront with the public hasn’t helped either. An excoriating October New Yorker investigation into the early years of the Google self-driving research project that eventually became Waymo found that the company had performed reckless road tests early in its work — and hadn’t always reported accidents.
Road Ahead
Musk’s promise to accelerate fully autonomous research, along with a call for more internal Tesla testers for the program, run precisely counter to that narrative. That’s not surprising: the eccentric Musk is known for imagining futures that are still years away — and using his wealth and influence to attempt to steer history toward or away from them.
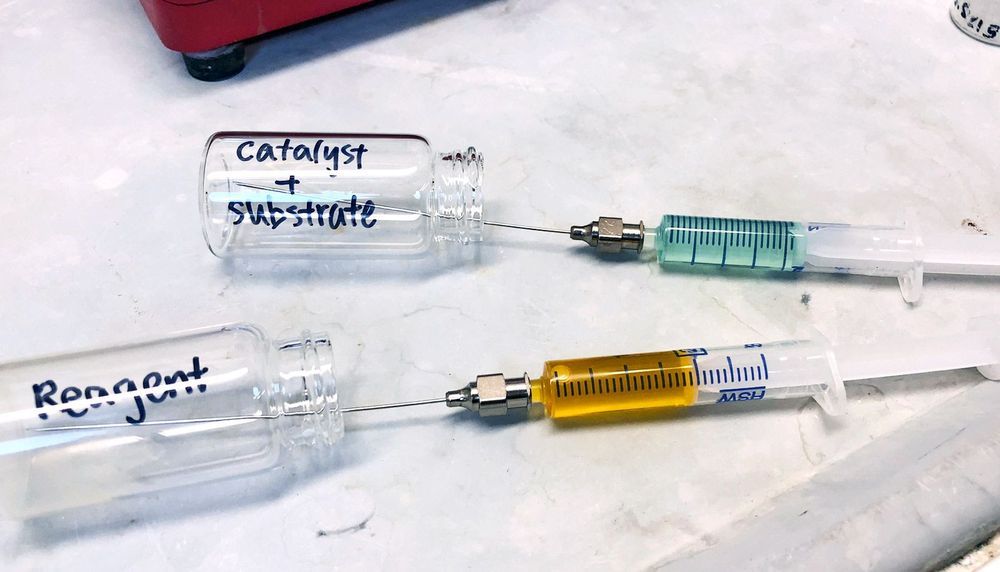
The paper is the latest in a series demonstrating the ability to use a dirhodium catalyst to selectively functionalize C-H bonds in a streamlined manner, while also maintaining virtually full control of the three-dimensional shape of the molecules produced.
“This latest catalyst is so selective that it goes cleanly for just one C-H bond—even though there are several C-H bonds very similar to it within the molecule,” says senior author Huw Davies, professor of organic chemistry. “That was a huge surprise, even to us.”
This dirhodium catalyst works on a substrate of tert-butyl cyclohexane, a hydrocarbon—one of the simplest of organic molecules, consisting entirely of C-H bonds.


WASHINGTON (AP) — Most Americans say it would be OK to use gene-editing technology to create babies protected against a variety of diseases — but a new poll shows they’d draw the line at changing DNA so children are born smarter, faster or taller.
A month after startling claims of the births of the world’s first gene-edited babies in China, the poll by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research finds people are torn between the medical promise of a technology powerful enough to alter human heredity and concerns over whether it will be used ethically.
Jaron Keener, a 31-year-old exhibit designer at Pittsburgh’s Carnegie Museum of Natural History, said he’s opposed to “rich people being able to create designer babies.”