Here are some ways to stay healthy amid the smoke and smog from California’s wildfires.



The brain has always been considered the main inspiration for the field of artificial intelligence(AI). For many AI researchers, the ultimate goal of AI is to emulate the capabilities of the brain. That seems like a nice statement but its an incredibly daunting task considering that neuroscientist are still struggling trying to understand the cognitive mechanism that power the magic of our brains. Despite the challenges, more regularly we are seeing AI research and implementation algorithms that are inspired by specific cognition mechanisms in the human brain and that have been producing incredibly promising results. Recently, the DeepMind team published a paper about neuroscience-inspired AI that summarizes the circle of influence between AI and neuroscience research.
You might be wondering what’s so new about this topic? Everyone knows that most foundational concepts in AI such as neural networks have been inspired by the architecture of the human brain. However, beyond that high level statement, the relationship between the popular AI/deep learning models we used everyday and neuroscience research is not so obvious. Let’s quickly review some of the brain processes that have a footprint in the newest generation of deep learning methods.
Attention is one of those magical capabilities of the human brain that we don’t understand very well. What brain mechanisms allow us to focus on a specific task and ignore the rest of the environment? Attentional mechanisms have become a recent source of inspiration in deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks(CNNs) or deep generative models. For instance, modern CNN models have been able to get a schematic representation of the input and ignore irrelevant information improving their ability of classifying objects in a picture.

On Tuesday, a team from China’s Hefei Institutes of Physical Science announced that its Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) reactor — an “artificial sun” designed to replicate the process our natural Sun uses to generate energy — just hit a new temperature milestone: 100 million degrees Celsius (180 million degrees Fahrenheit).
For comparison, the core of our real Sun only reaches about 27 million degrees Fahrenheit — meaning the EAST reactor was, briefly, more than six times hotter than the closest star.

Two possibilities: Either the image captures two massive galactic clusters in the process of colliding, or NASA is covering up the existence of a starship so big it’s several million light years long.
Humanity’s current understanding of physics may suggest faster-than-light travel is impossible, but researchers here on Earth can still observe happening in places much too far away to ever actually visit (and generally only what they looked like in the distant past). One of them is a galactic collision that, at least from our planetary vantage point, looks an awful lot like a craft going where no man has ever gone before.
NASA released the above composite image of the galaxy cluster Abell 1033 some 1.62 billion light years away this week, showing wisps of gas that appear to be arranged in the shape of Star Trek’s USS Enterprise. NASA wrote that the image was captured by the Chandra X-ray Observatory, an X-ray telescope that detects superheated gases, as well as the Low-Frequency Array, which detects radio emissions.
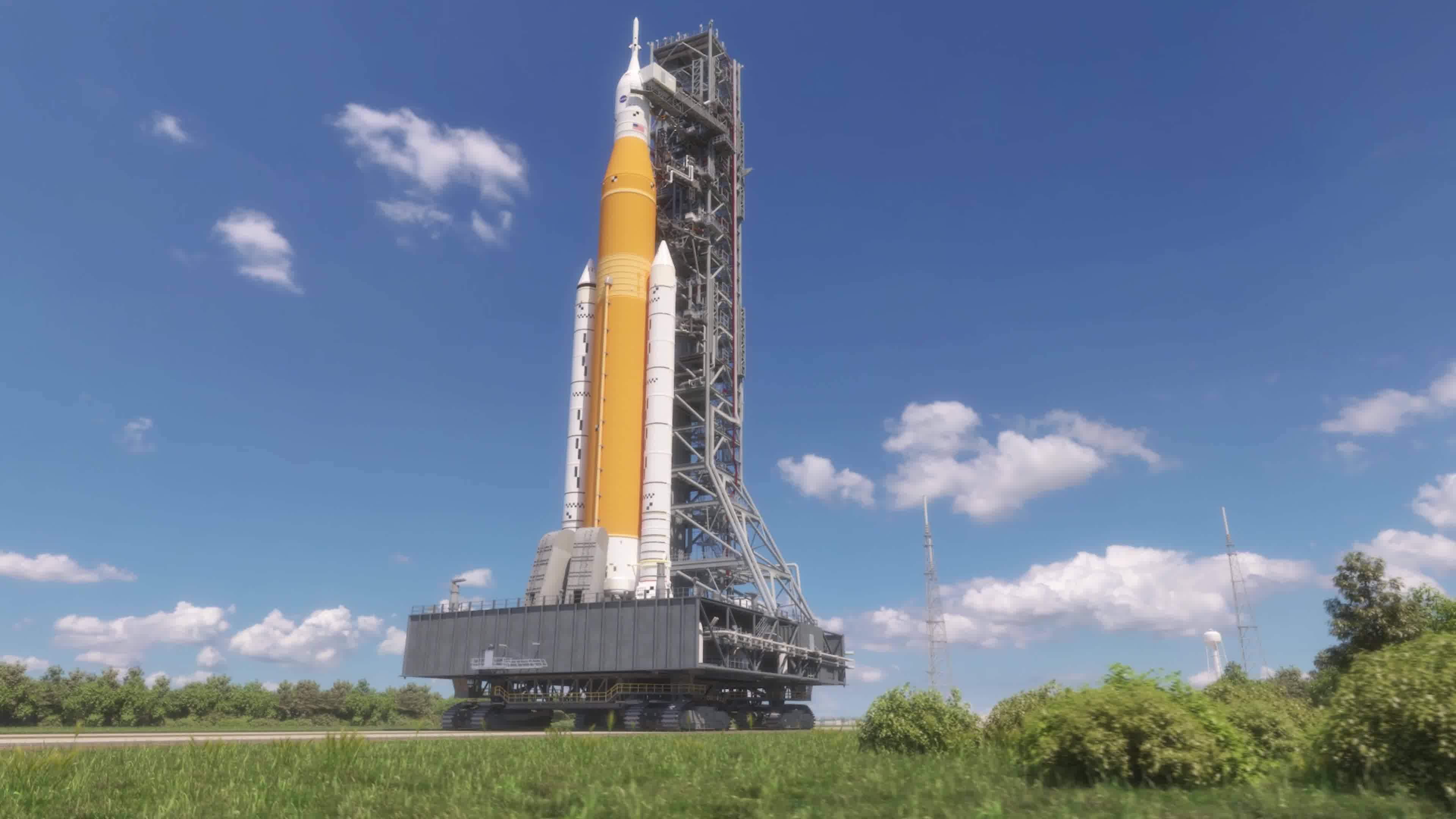

Click on photo to start video.
NASA’s Rocket Science in 60 Seconds gives you an inside look at work being done to explore deep space. In the latest episode you can hear Rob Stough, payload utilization manager for our NASA’s Space Launch System, talk about the power we needed to boost the rocket into space and send NASA’s Orion Spacecraft to the Moon. Watch: https://youtu.be/0VB9aI3xVFs

In a tweet, Saturday, SpaceX founder Elon Musk announced that “radical change” was coming to the design of the Big Falcon Rocket (BFR), that is being made in an attempt to go to Mars.
Musk left out any specifics of his plan, simply announcing that “SpaceX is no longer planning to upgrade Falcon 9 second stage for reusability” and would be “Accelerating BFR instead.” Musk called the new design “very exciting” and “delightfully counter-intuitive.”