A new Psyence BioMed program will test whether psilocybin can shift real aging biomarkers, from inflammation to mitochondria. Here’s what science says so far.



For half a century, scientists struggled to predict how proteins fold. A puzzle at the heart of understanding life and curing disease. Then, five years ago, the #alphafold team cracked the code.
Since then, more than 3 million researchers across 190+ countries have used AlphaFold’s freely available database of 200 million+ protein structures, accelerating discoveries in everything from drug design to disease-resistant crops, bee conservation, and plastic-eating enzymes.
Further reading:
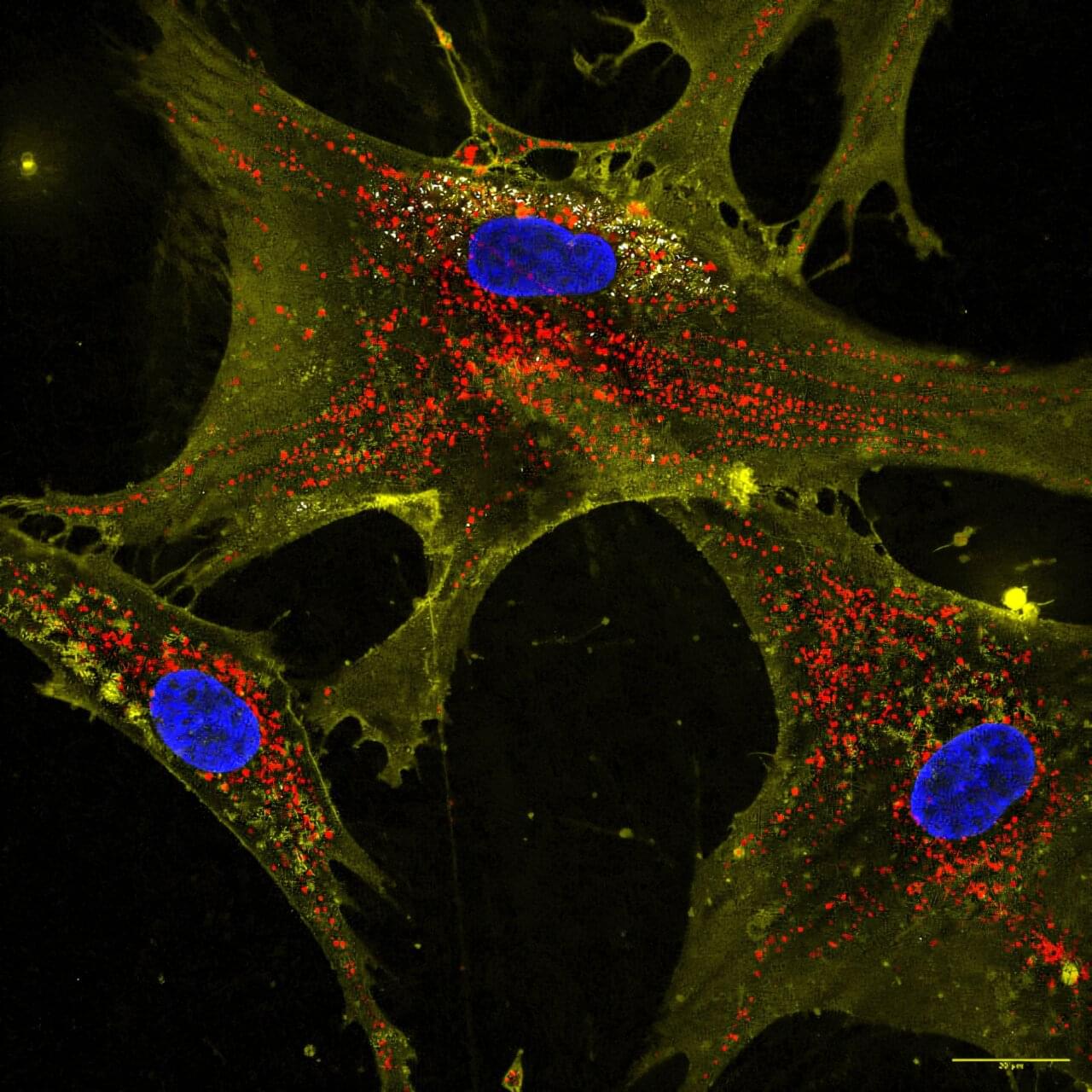
Biomedical researchers at Texas A&M University may have discovered a way to stop or even reverse the decline of cellular energy production—a finding that could have revolutionary effects across medicine.
Dr. Akhilesh K. Gaharwar and Ph.D. student John Soukar, along with their fellow researchers from the Department of Biomedical Engineering, have developed a new method to give damaged cells new mitochondria, returning energy output to its previous levels and dramatically increasing cell health.
Mitochondrial decline is linked to aging, heart disease and neurodegenerative disorders. Enhancing the body’s natural ability to replace worn-out mitochondria could fight all of them.
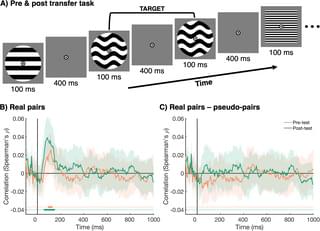
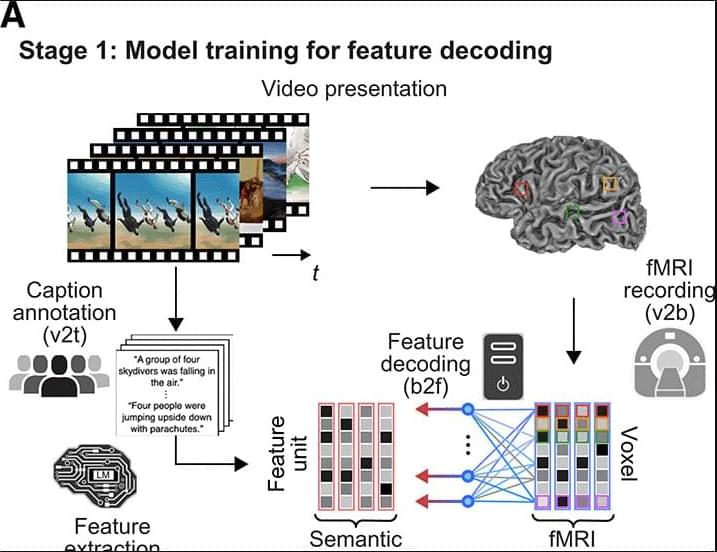
How do brains align during social interaction to support shared understanding? This study shows that interbrain information alignment emerges rapidly and strengthens with practice, with distinct neural processes supporting sensory synchrony during early alignment and shared cognitive representation in real pairs during late alignment.

npj Artificial Intelligence has APC waivers available that can be allocated upon acceptance on an ad-hoc basis. For additional information, contact the Journal Publisher, Ronghua Guo.