💡 LastestPaper.
🧑🏻🔬 By Ms. Cloe García Porta, Dr. Kashif Mahfooz, Mr. Joanna Komorowska, Dr. Sara Garcia-Rates and Dr. Susan Greenfield.
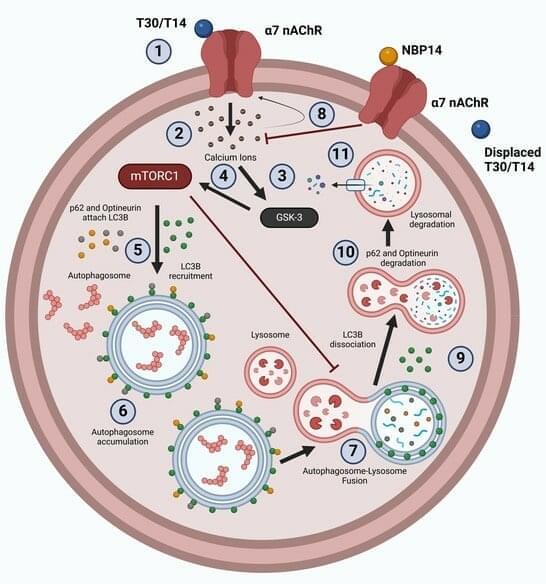
During development, a 14mer peptide, T14, modulates cell growth via the α-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7 nAChR). However, this process could become excitotoxic in the context of the adult brain, leading to pathologies such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Recent work shows that T14 acts selectively via the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). This pathway is essential for normal development but is overactive in AD. The triggering of mTORC1 has also been associated with the suppression of autophagy, commonly observed in ageing and neurodegeneration. We therefore investigated the relationship between T14 and autophagic flux in tissue cultures, mouse brain slices, and human Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus.