A new study found that an enzyme involved in protein translation is essential for circulating immune cells, called monocytes, to mature into tissue-resident macrophages, a specialized population of immune cells that maintain organ health by clearing dead cells and debris. Without this enzyme, monocytes enter tissues but fail to fully differentiate, leading to impaired tissue maintenance and persistent immune cell infiltration that causes inflammation instead of repair.
The research, published in Nature, showed that deoxyhypusine synthase (DHPS) is required for both the differentiation and long-term survival of macrophages across multiple organs, including the lung, liver, brain, kidney, heart and peritoneal cavity.
Using a series of mouse models, the investigators demonstrated that DHPS controls a core, tissue-agnostic program that enables macrophages to adhere to their local environment, interact with surrounding cells and carry out the essential functions that maintain tissue balance and organ health.
The researchers traced these defects to the polyamine–hypusine pathway. Analyses of gene activity, protein production and protein-making machinery revealed that DHPS is required for efficient translation of a subset of genes involved in cell adhesion (the ability to stick to their surroundings and to other cells so they can stay in the correct place and function properly), signaling, and tissue interaction. Without DHPS, macrophages failed to express key proteins needed to anchor themselves within tissues and respond appropriately to local cues.
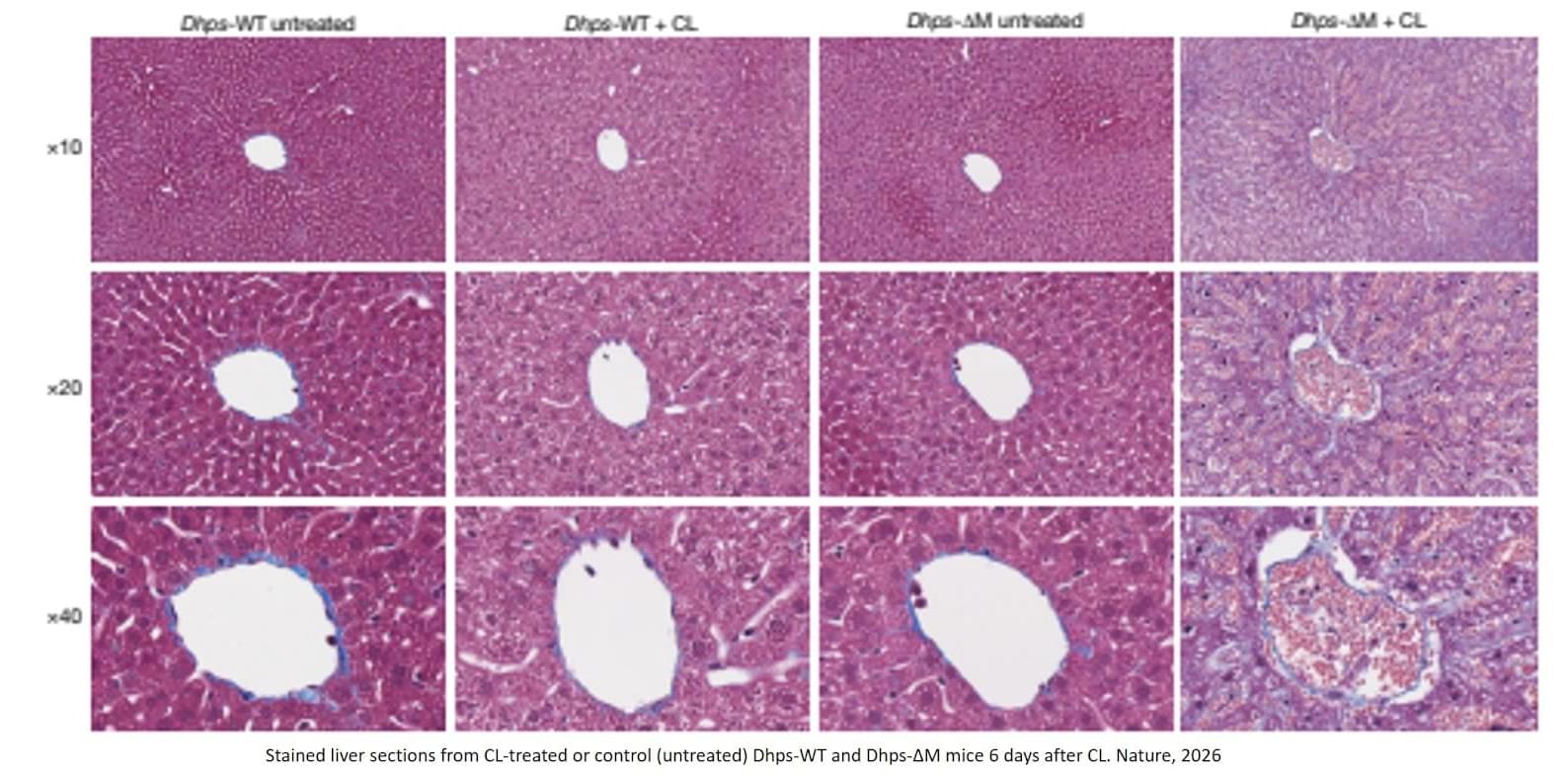
Imaging studies showed that DHPS-deficient macrophages had abnormal shape and positioning within tissues, while functional assays demonstrated defects in the clearance of dead cells and tissue maintenance. In the lung, this impairment led to accumulation of surfactant material, a substance in the lungs that keeps air sacs open, and immune cell infiltration, while in the liver, acute macrophage depletion followed by failed restoration resulted in vascular disruption and tissue damage. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission.