A new device at the University of Central Florida captures carbon dioxide and turns it into useful products.
Category: sustainability – Page 115

China’s Dominance in the Solar Panel Supply Chain
You might’ve heard comments about how western powers have been falling behind in the solar game. This chart shows how very real the Chinese dominance in that field is! Source:
The supply chain is key for the renewable energy revolution, and this chart visualizes where the world’s solar panels are manufactured.
New storage solution poised to revolutionize the energy sector with groundbreaking thermal technology: ‘Critical to reach net-zero’
An innovative thermal energy storage system uses sand to store and release renewable energy without traditional batteries.

Revolutionizing E-Waste Recycling: New Methods for Metal Recovery
How can electronic waste, also known as e-waste, be recycled without resulting in negative environmental impacts that are often produced with traditional e-waste recycling methods? This is what a recent study published in Nature Chemical Engineering hopes to address as a team of researchers from Rice University investigated a novel approach for improving e-waste recycling while mitigating the negative impacts on the environment. This study holds the potential to help researchers, climate conservationists, and the public better understand how they can contribute to a cleaner environment through recycling.
“Our process offers significant reductions in operational costs and greenhouse gas emissions, making it a pivotal advancement in sustainable recycling,” said Dr. James Tour, who is a T.T. and W.F. Chao Professor of Chemistry at Rice University and a co-author on the study.
For the study, the team built upon past research conducted by Dr. Toru involving flash joule heating (FJH), which uses electric currents to break down metals into other materials. Using FJH for e-waste, the researchers successfully removed precious metals, including tantalum, indium, and gallium, which have commercial uses in capacitors, LCD displays, and semiconductors, respectively. Additionally, this new method was found to provide increased efficiency for metal purity and number of metals, also called yield, at 95 percent and 85 percent, respectively, along with significantly reducing environmental harm since this method does not require acids or water for its reaction.

Fossil Fuels and the Arctic: Uncovering the Impact of Air Pollution
“Our study is a stark example of how air pollution can substantially alter atmospheric chemistry thousands of miles away,” said Jacob Chalif.
How do fossil fuels influence the atmospheric chemistry of the Arctic? This is what a recent study published in Nature Geoscience hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated how air pollution caused by fossil fuels influences levels of methanesulfonic acid (MSA), which is an airborne byproduct of marine phytoplankton. This study has the potential to help researchers, climate scientists, and the public better understand the long-term consequences of fossil fuels and the steps that can be taken to mitigate them.
This study builds on several past studies, specifically a 2013 ice core research study from Denali National Park, that hypothesized reduced MSA levels resulted from drastic reductions in phytoplankton during the same period. However, the researchers ruled out a connection between MSA and phytoplankton populations but were still puzzled about the drops in MSA levels in the Arctic.

World’s first AI art museum to explore ‘creative potential of machines’ in LA
Dataland co-founder Refik Anadol, 38, is a media artist whose “crowd-pleasing – and controversial” works using artificial intelligence have been displayed around the world, including at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, the Serpentine and, most recently, the United Nations headquarters.
In the past two years, Anadol has found himself at the center of debates over the value of AI-generated art, as crowds have been reportedly “transfixed” by his massive interactive digital canvases, while some art critics have panned them as over-hyped and mediocre.
Now Anadol is looking to build artists like himself a permanent exhibition space among some of LA’s most prominent high-culture venues, and he is pledging that the AI art museum will promote “ethical AI” and use renewable energy sources.

Ultra-high speed camera for molecules: Attosecond spectroscopy captures electron transfer dynamics
In nature, photosynthesis powers plants and bacteria; within solar panels, photovoltaics transform light into electric energy. These processes are driven by electronic motion and imply charge transfer at the molecular level. The redistribution of electronic density in molecules after they absorb light is an ultrafast phenomenon of great importance involving quantum effects and molecular dynamics.

Rare Earth Metals Found in Extinct Volcanoes Could Power The Future
Extinct volcanoes are hard to study – we never see them erupt. Using a unique experimental technique, we were able to recreate a certain type of extinct volcano in a lab, learning more about the magma these volcanoes produce.
We found that some rare magma types are surprisingly efficient at concentrating rare earth elements. This is a group of metals with crucial applications in several high-tech industries, such as magnets for electric vehicles and wind turbines.
Demand for rare earths is soaring as society moves away from fossil fuels and electrifies energy production and transport. Despite the name, rare earths aren’t particularly rare. The biggest challenge is finding rocks in which these metals are concentrated enough to be economically viable to extract.

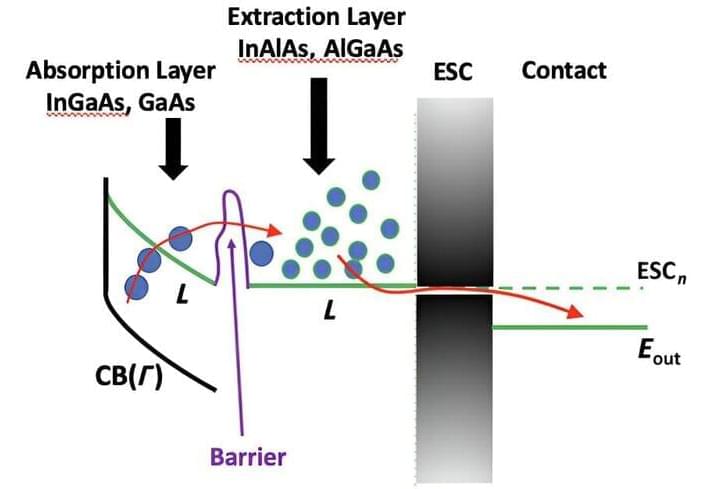
New insights into hot carrier solar cells: Study explores hot electron tunneling and collection to enhance efficiency
Hot carrier solar cells, a concept introduced several decades ago, have long been seen as a potential breakthrough in solar energy technology. These cells could surpass the Shockley–Queisser efficiency limit, which is a theoretical maximum efficiency for single-junction solar cells. Despite their promise, practical implementation has faced significant challenges, particularly in managing the rapid extraction of hot electrons across material interfaces.